- Filter By:
-
-
Stock photos and images of username:creativepic
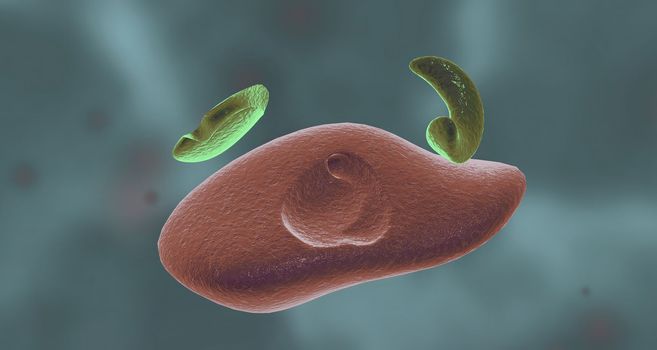
Bacteria are small single celled organisms.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5602x3066pxBacteria are small single celled organisms.
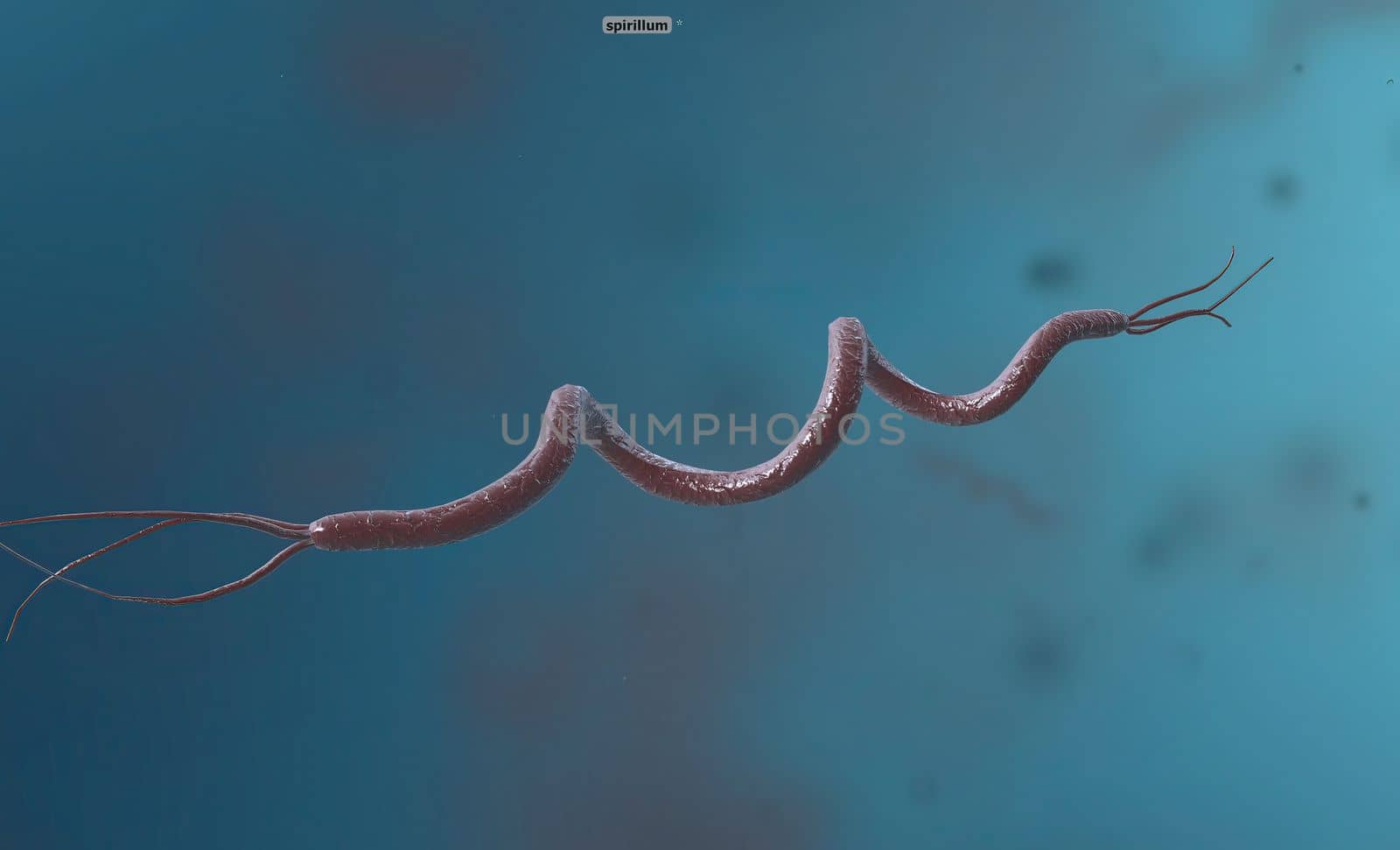
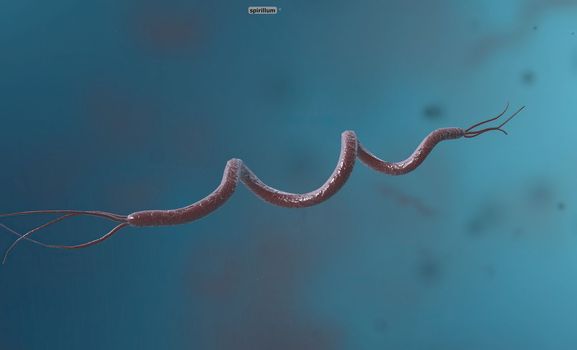
Spirillum is a bacterium from the Proteobacteria phylum with a spiral-shaped cell morphology.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5056x3068pxSpirillum is a bacterium from the Proteobacteria phylum with a spiral-shaped cell morphology.
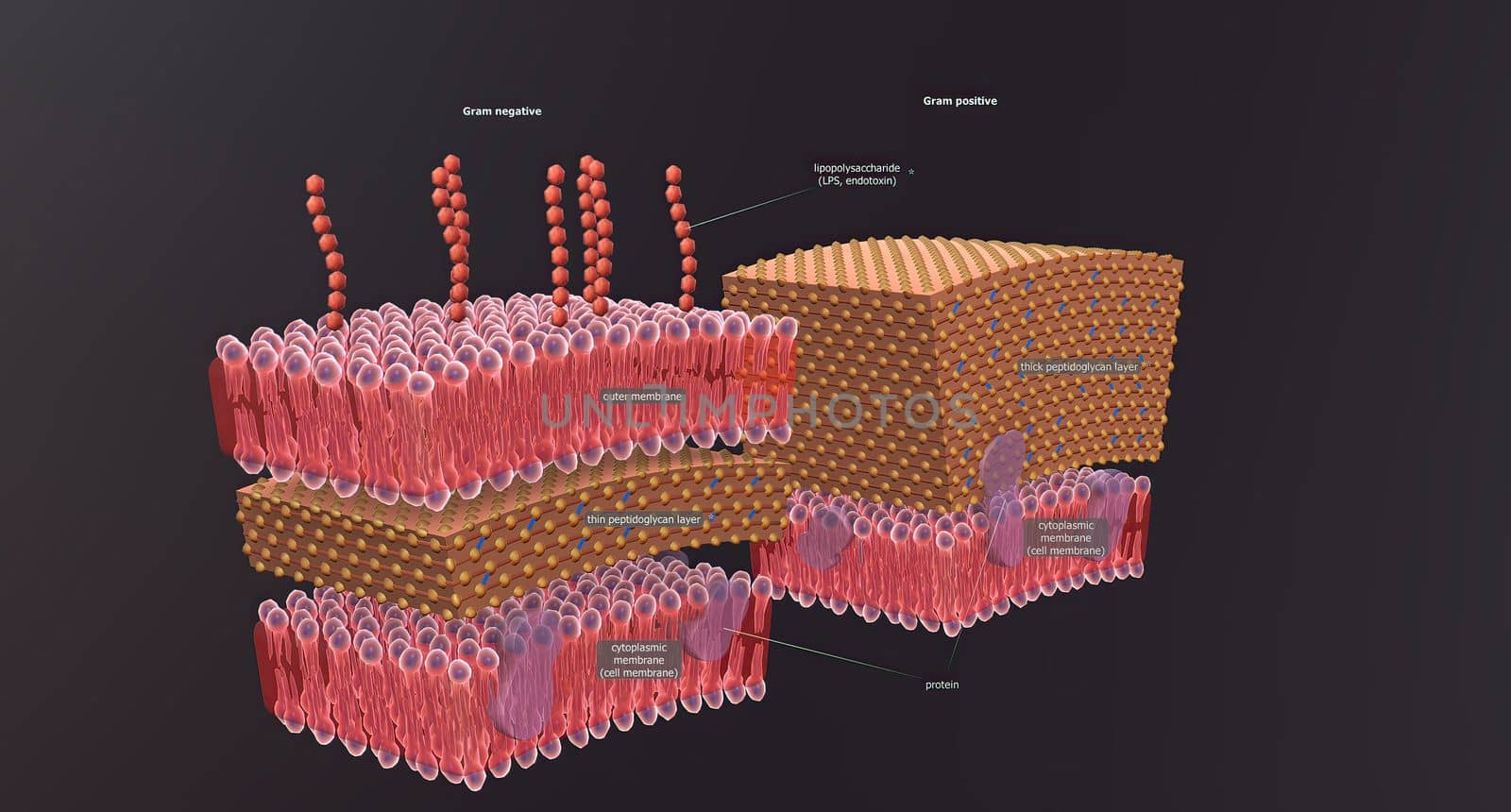
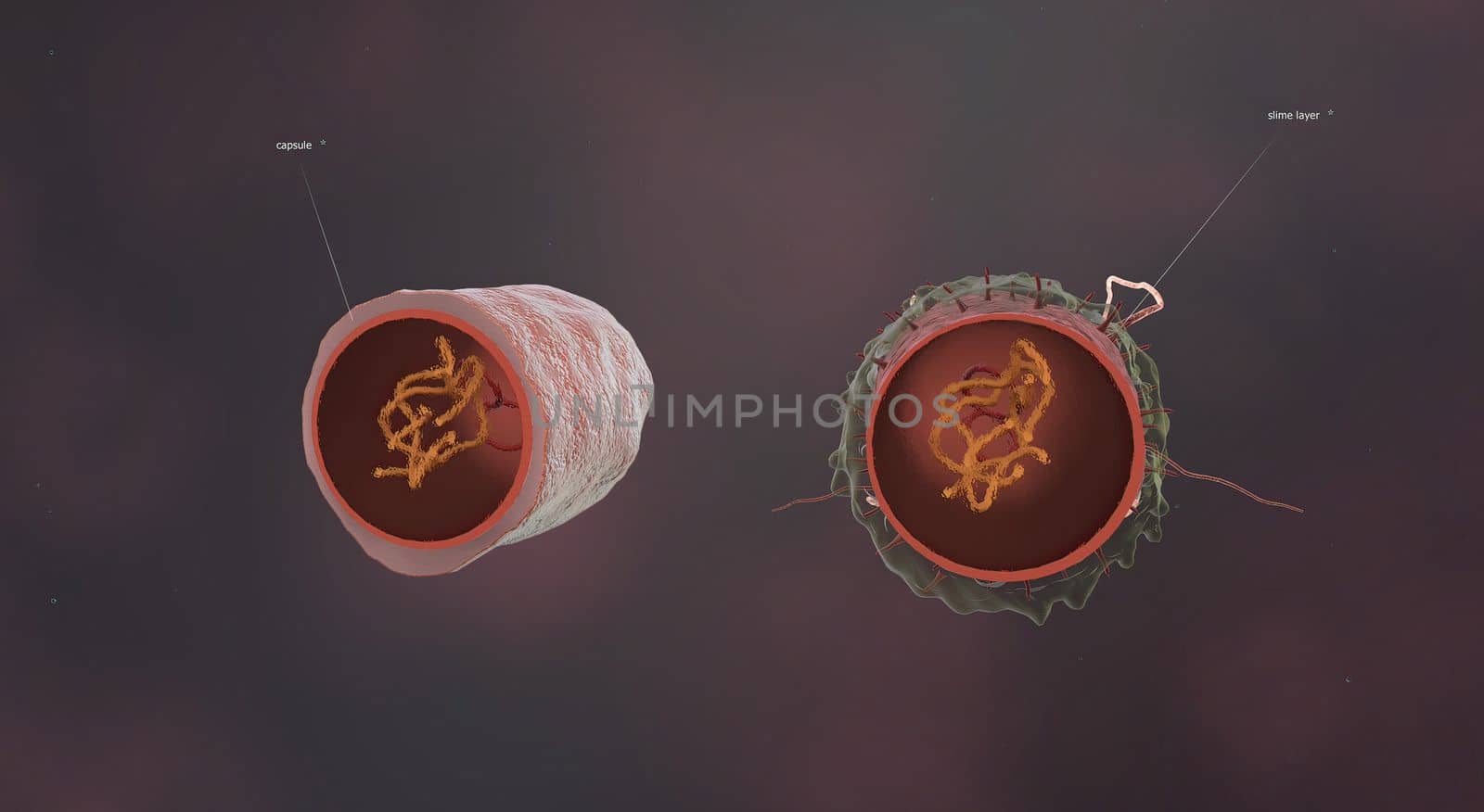
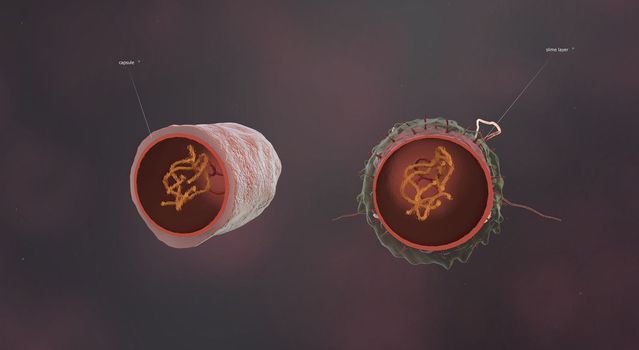
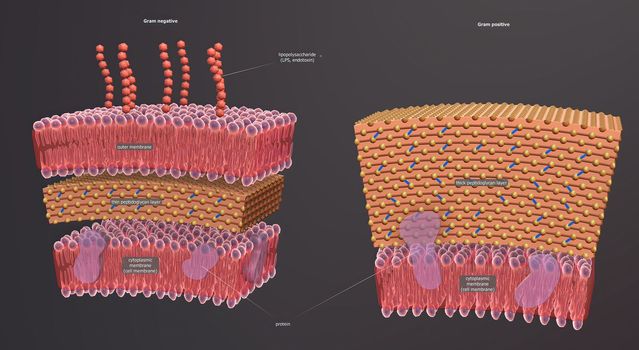
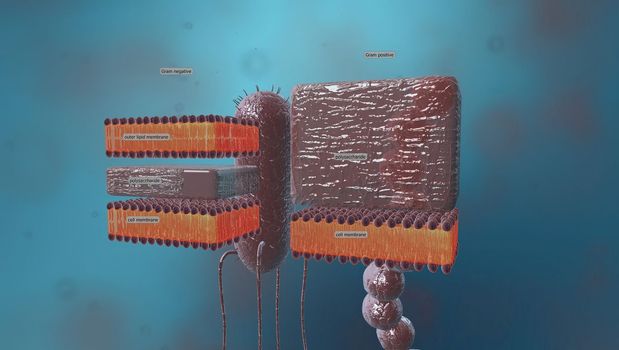
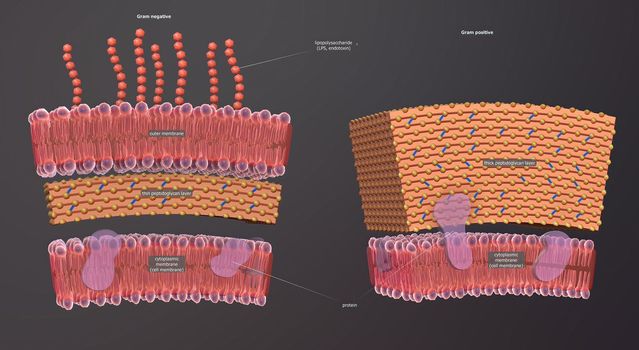
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5726x3076pxA cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
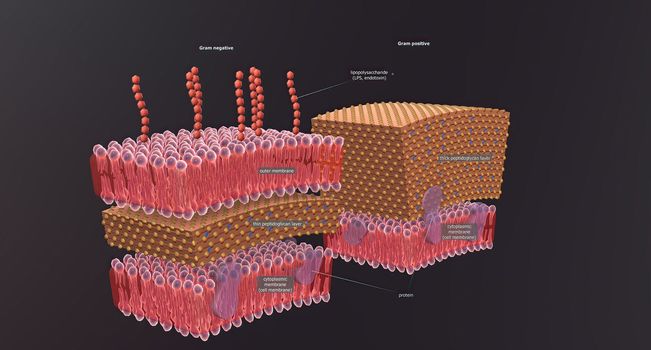
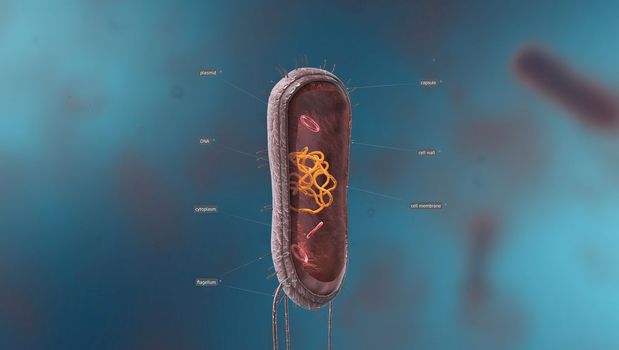
Bacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5726x3076pxBacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.

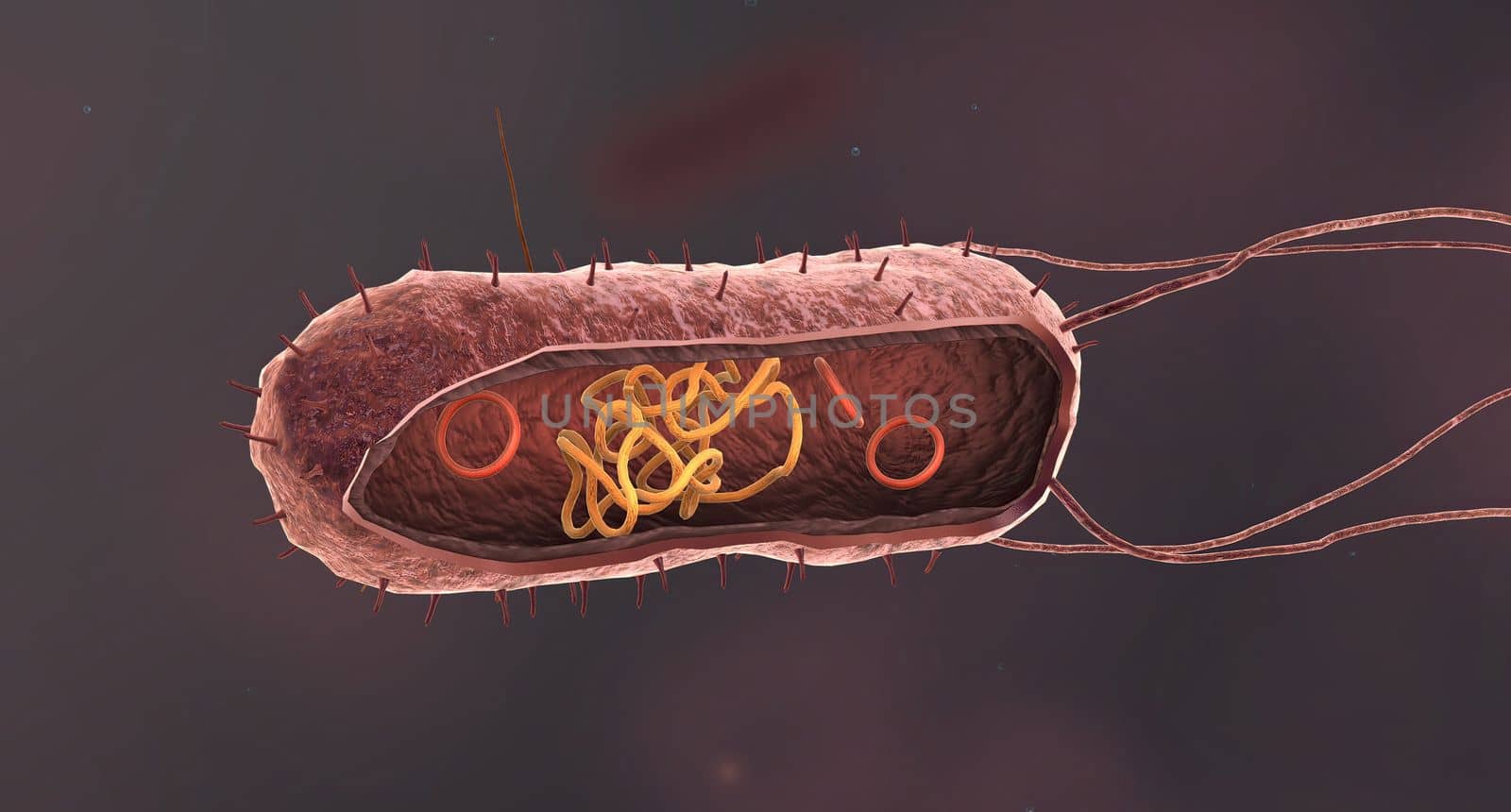
Bacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5426x3068pxBacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.

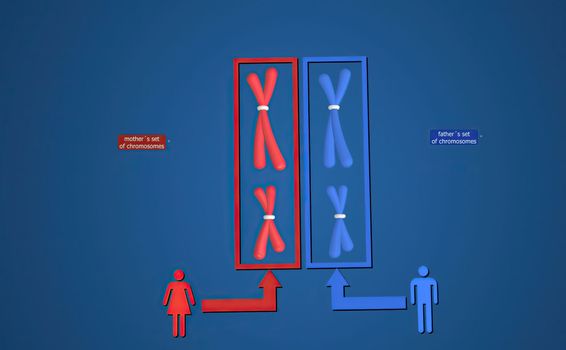
In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxIn cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxA virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism


A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
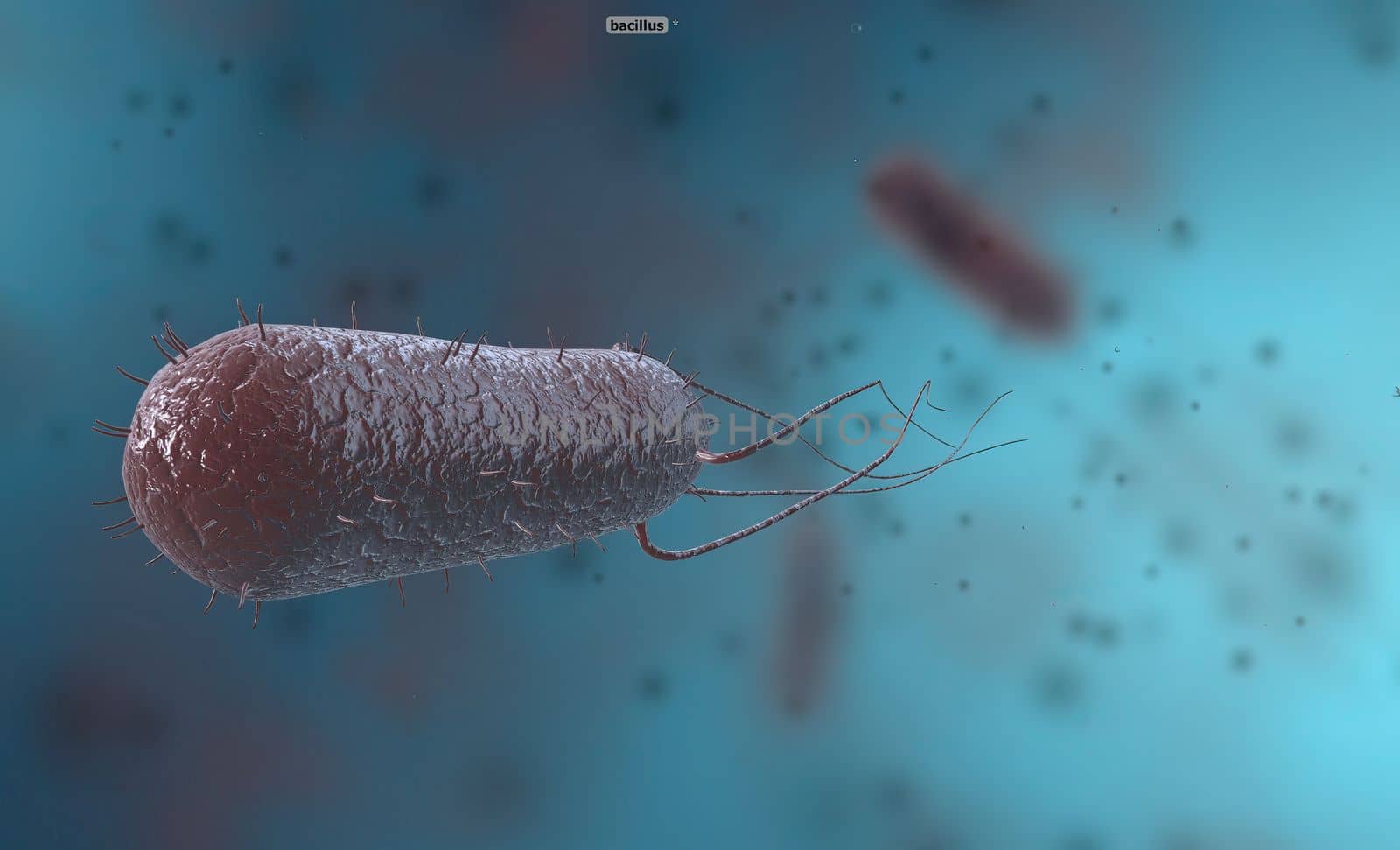
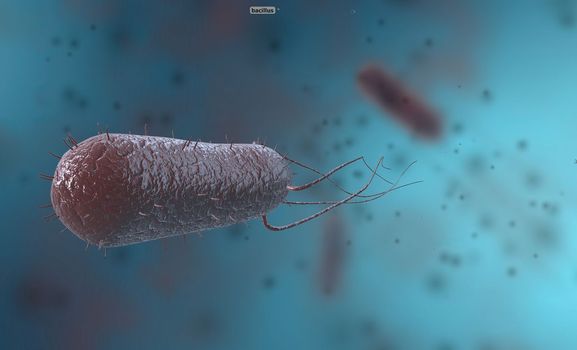
Bacillus is a gram-positive and spore-forming bacterium in the form of rods or rods.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5056x3068pxBacillus is a gram-positive and spore-forming bacterium in the form of rods or rods.
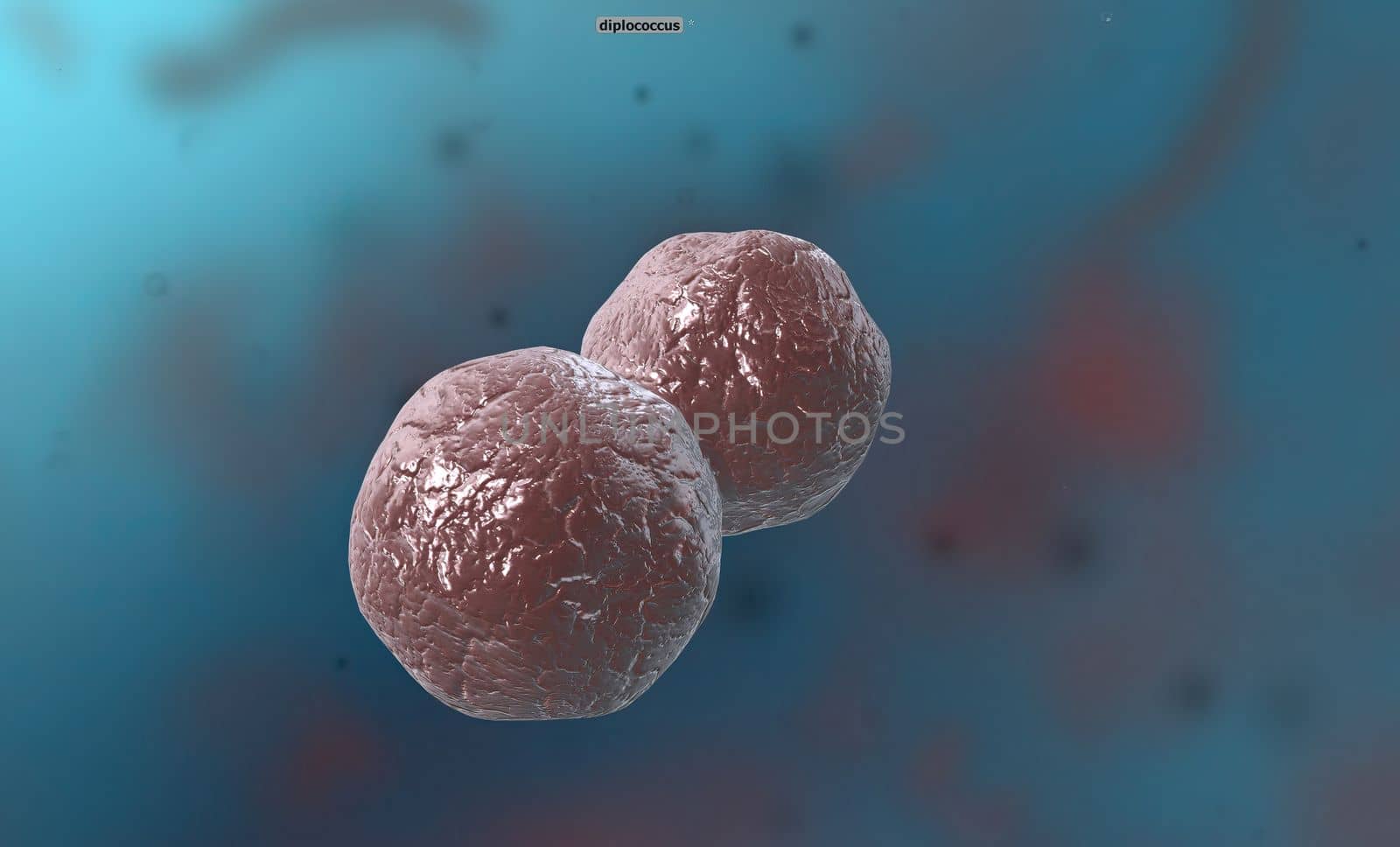
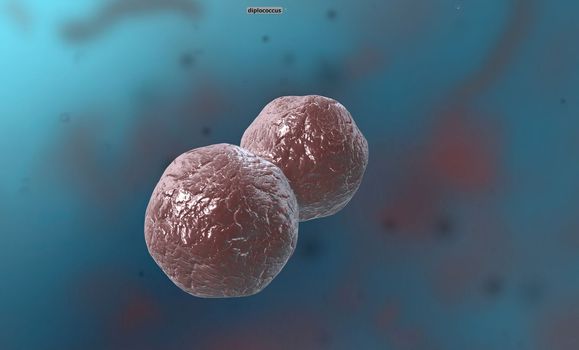
A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
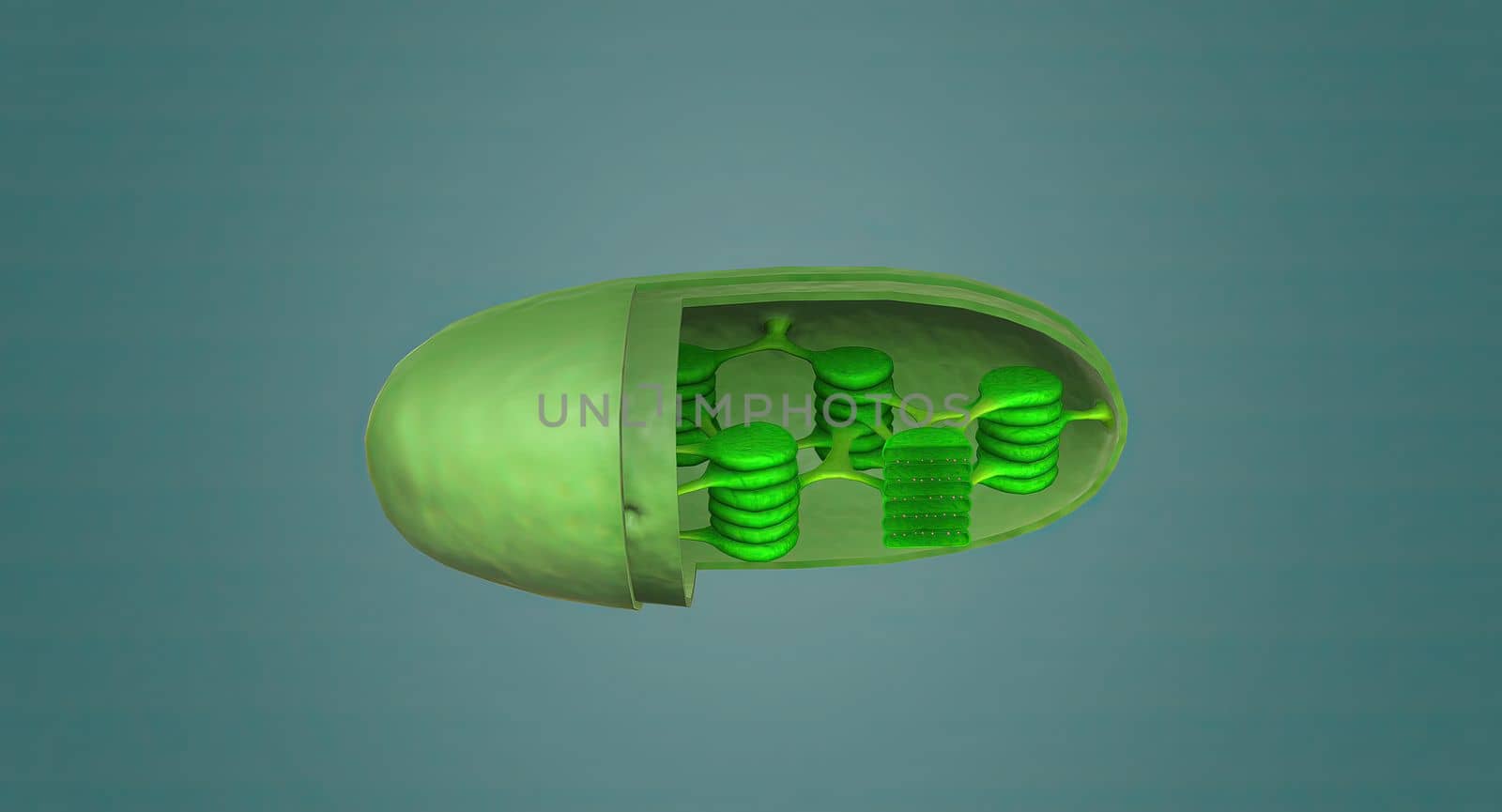

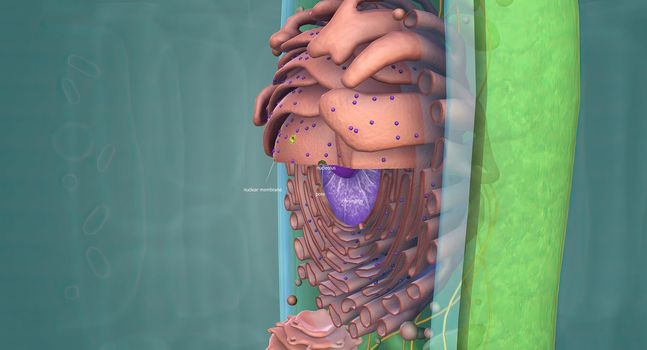
Mitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxMitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
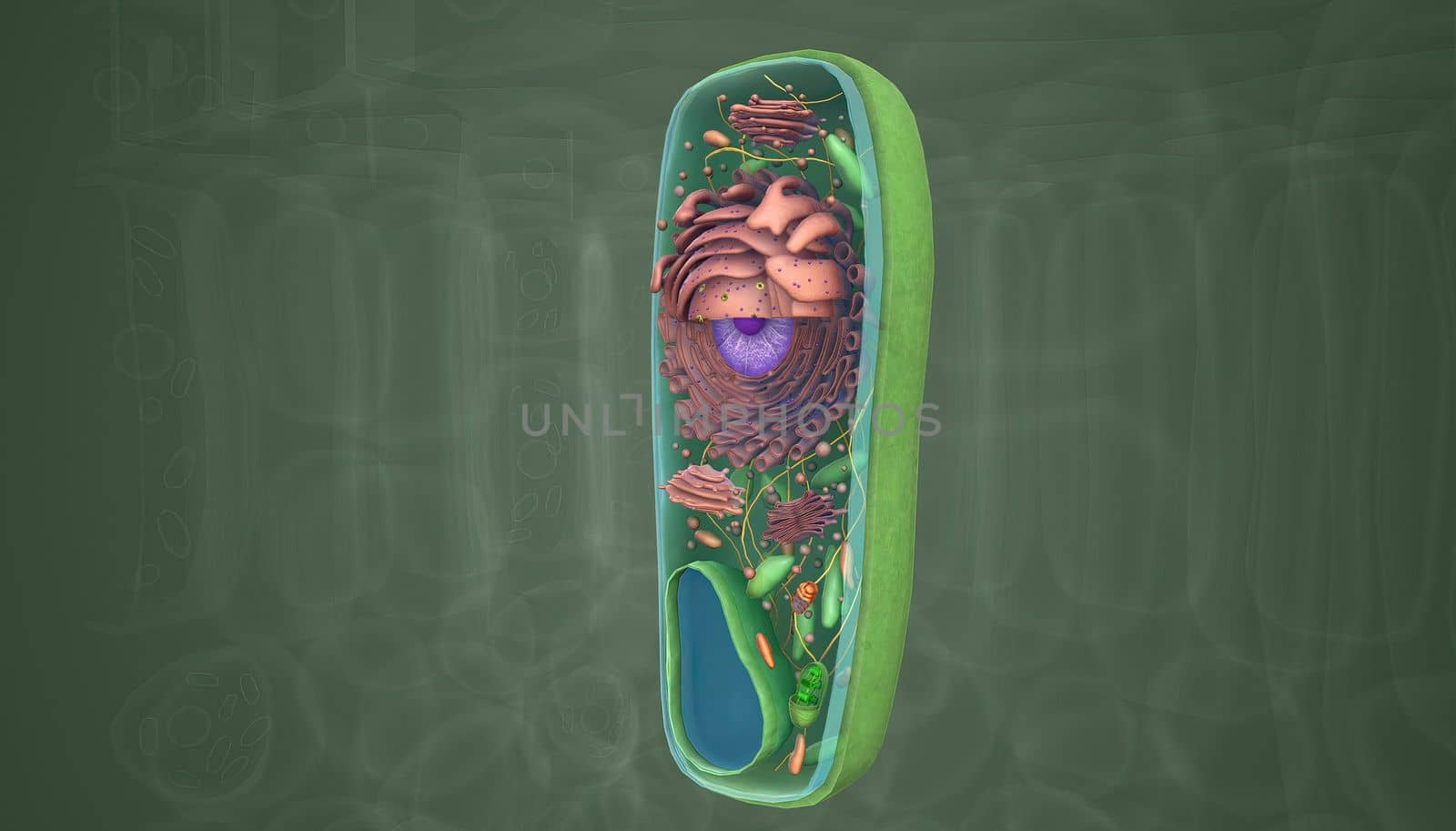
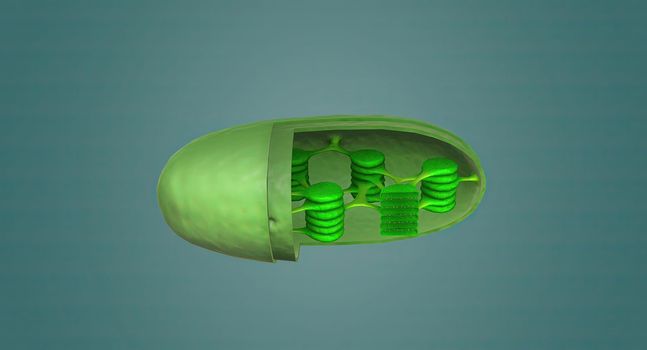

The cell is the basic unit of life. Plant cells are surrounded by a thick, rigid cell wall.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5414x3088pxThe cell is the basic unit of life. Plant cells are surrounded by a thick, rigid cell wall.
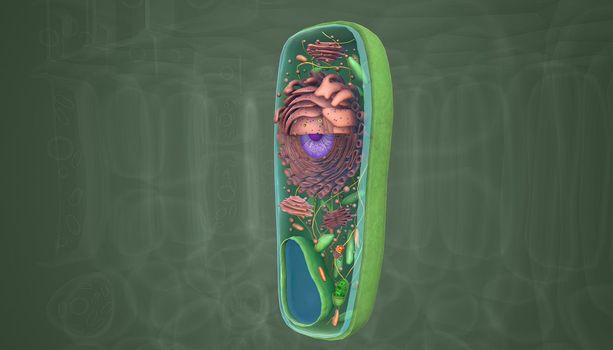

A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
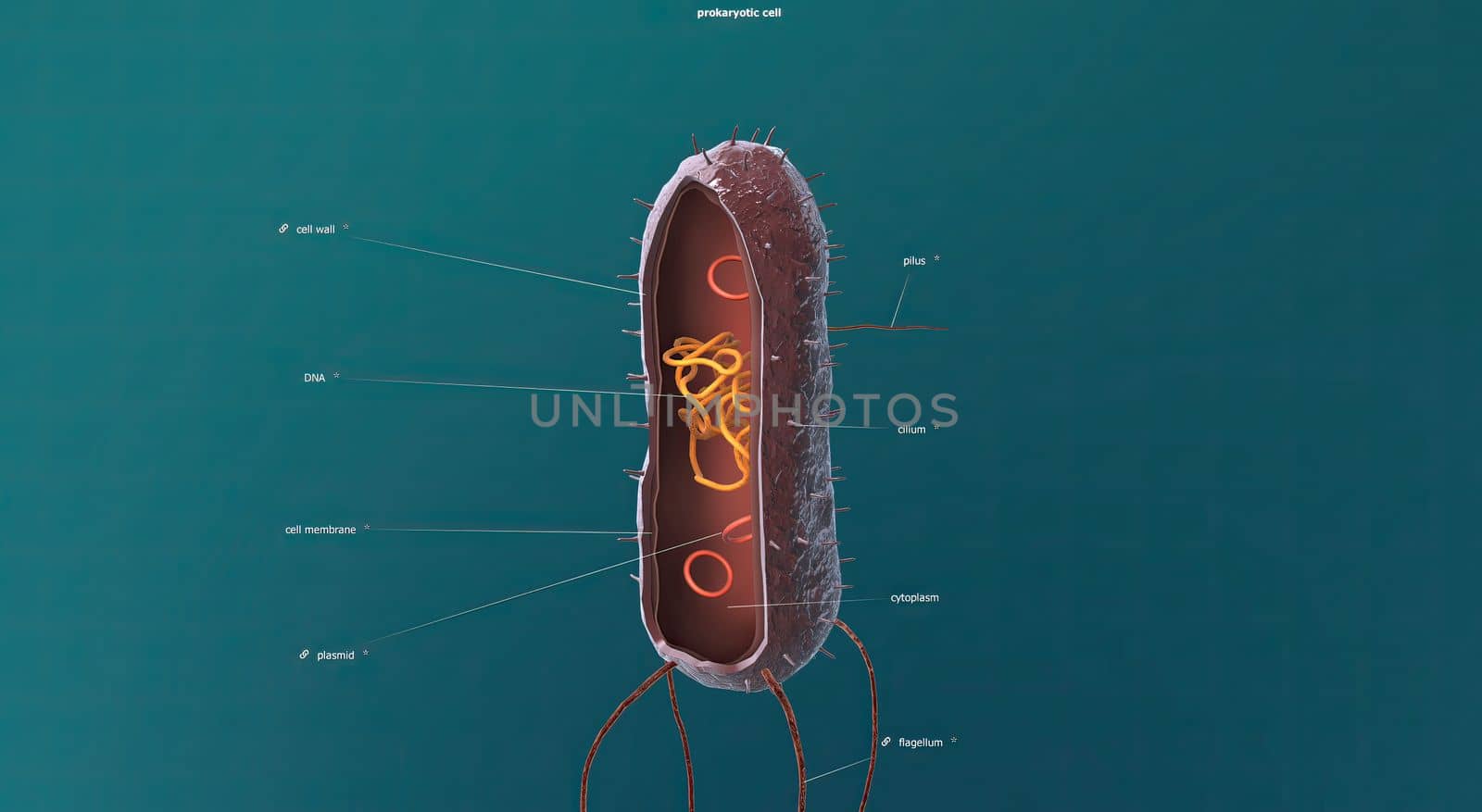
Bacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5726x3076pxBacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.

A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.

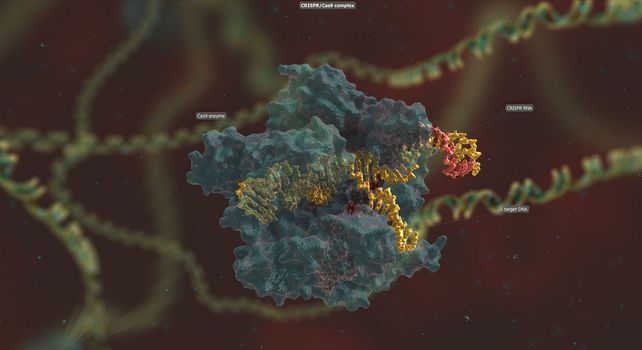
The long RNA backbone binds to the DNA, and the predesigned sequence guides Cas9 to the right spot in the genome.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5562x3030pxThe long RNA backbone binds to the DNA, and the predesigned sequence guides Cas9 to the right spot in the genome.
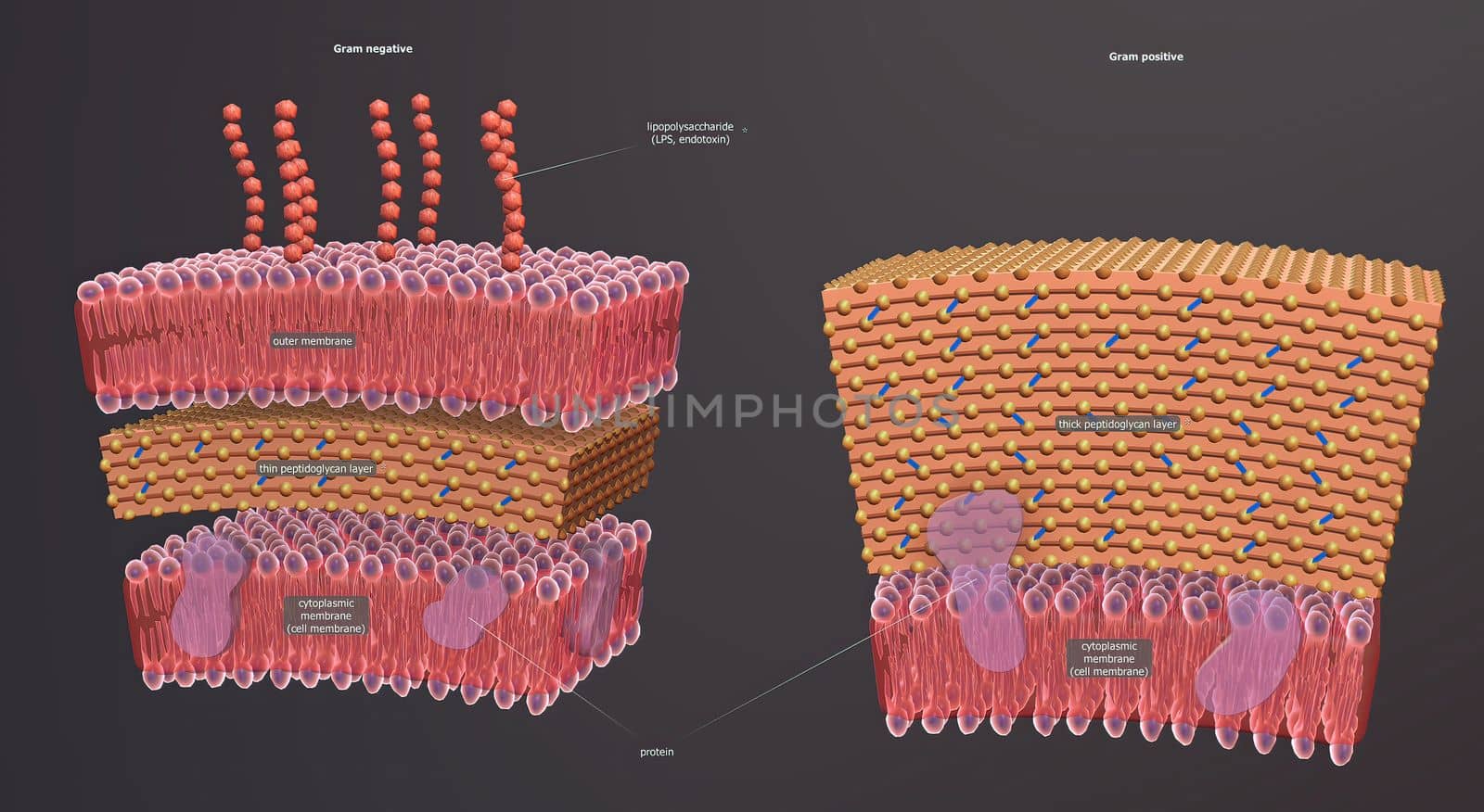
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5602x3066pxA cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
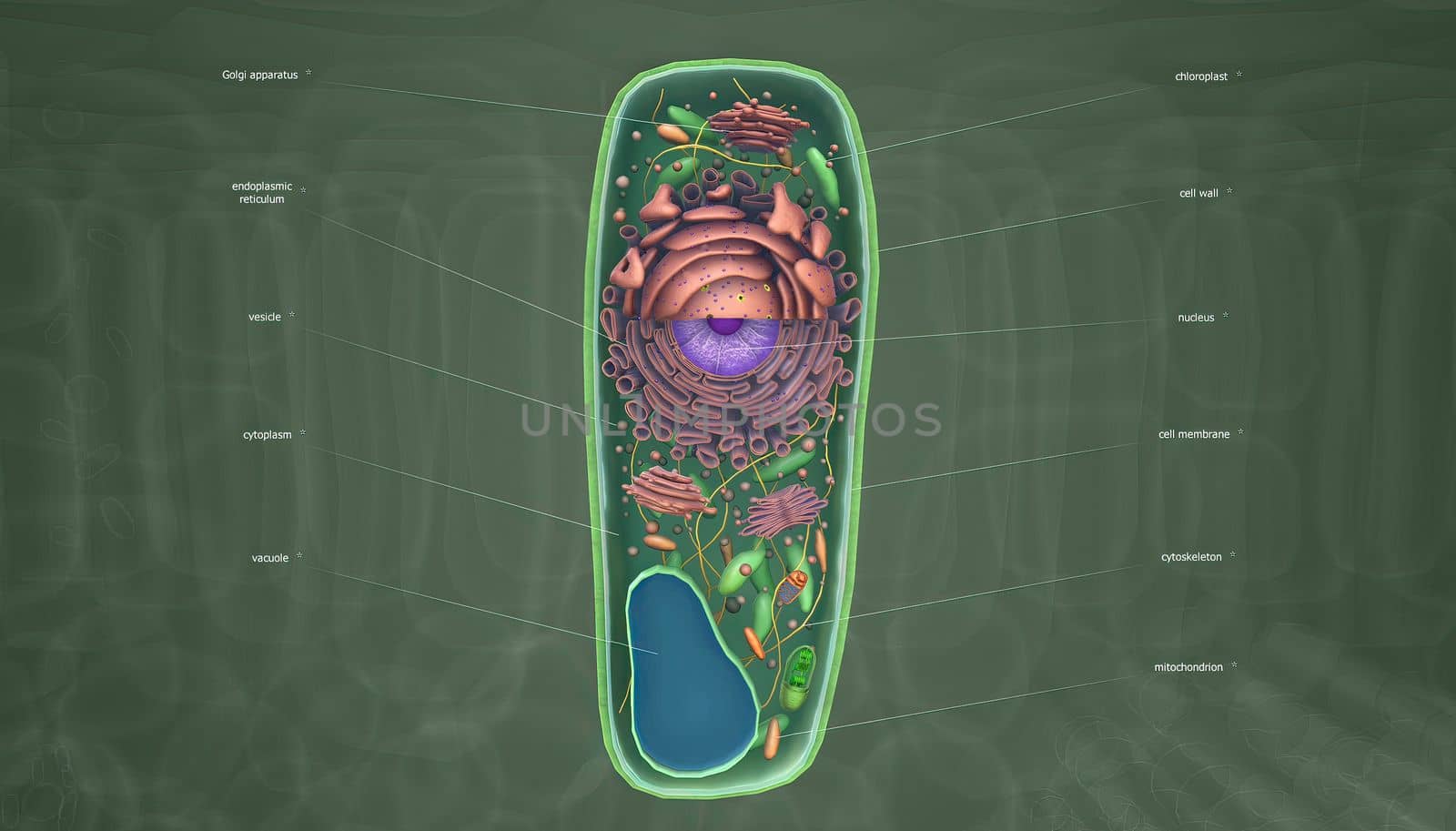
The cell is the basic unit of life. Plant cells are surrounded by a thick, rigid cell wall.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5414x3088pxThe cell is the basic unit of life. Plant cells are surrounded by a thick, rigid cell wall.
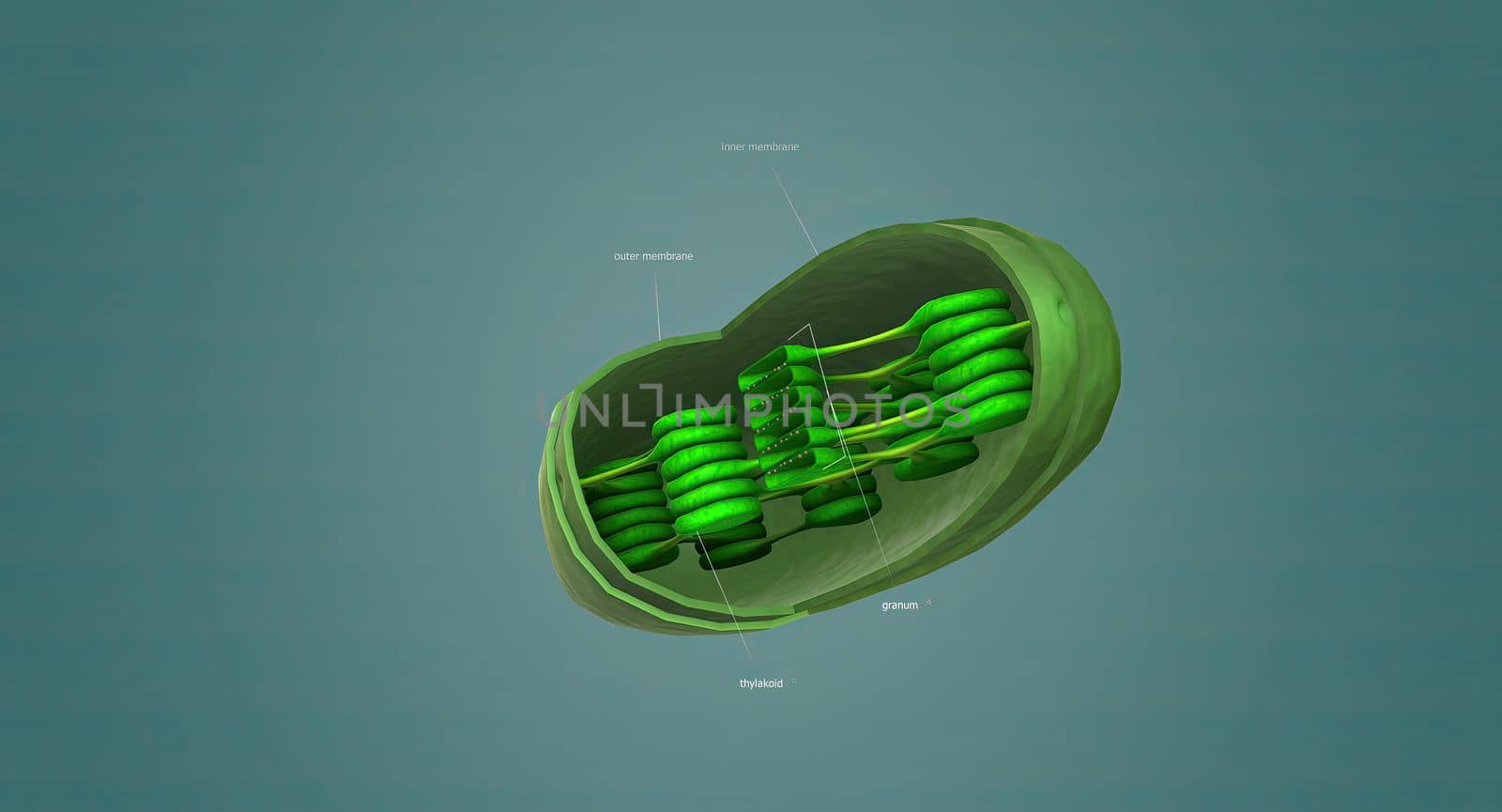
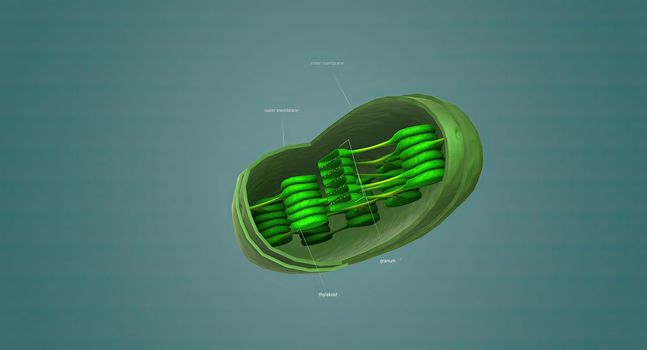
Mitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxMitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
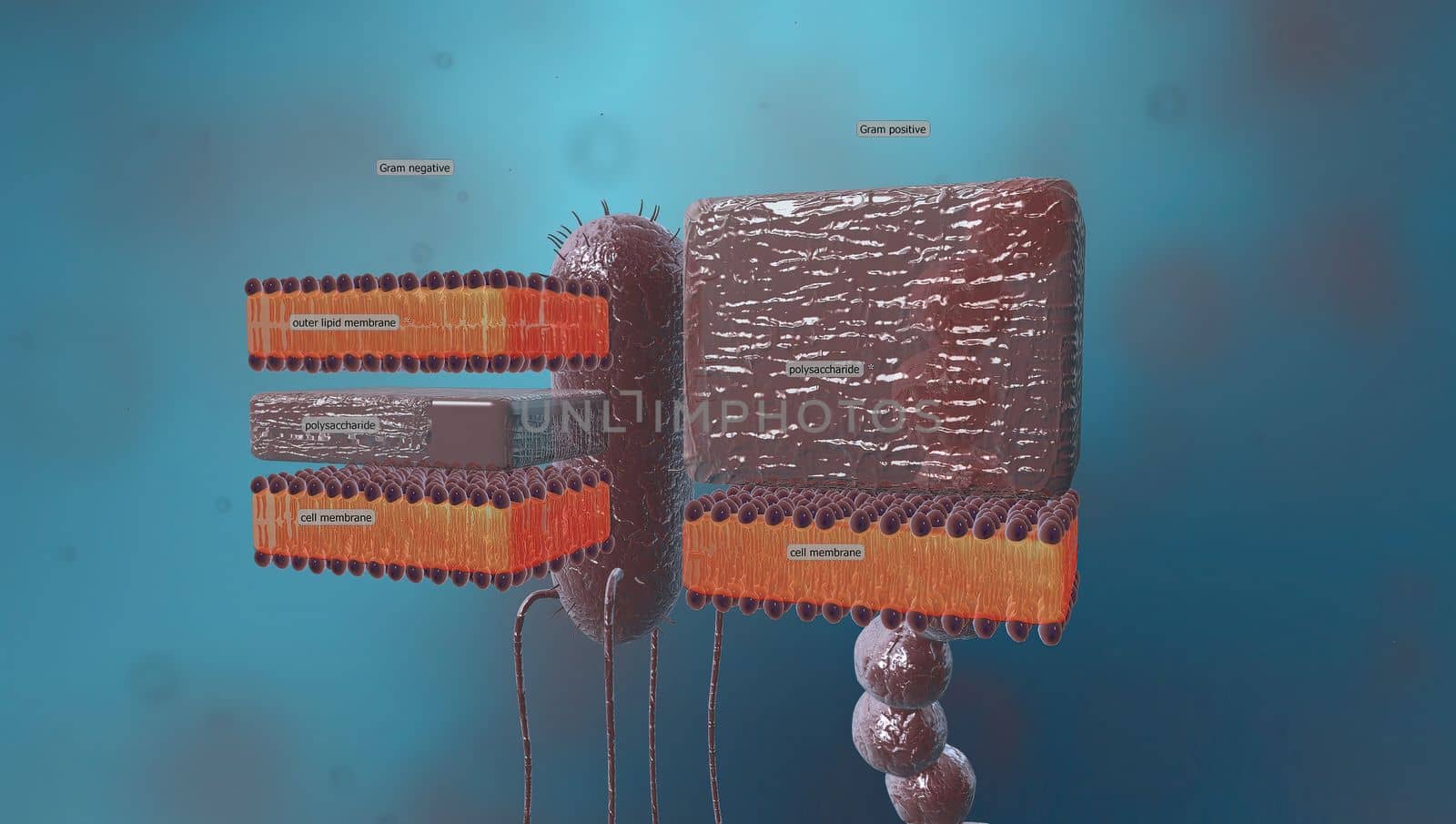
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5426x3068pxA cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.

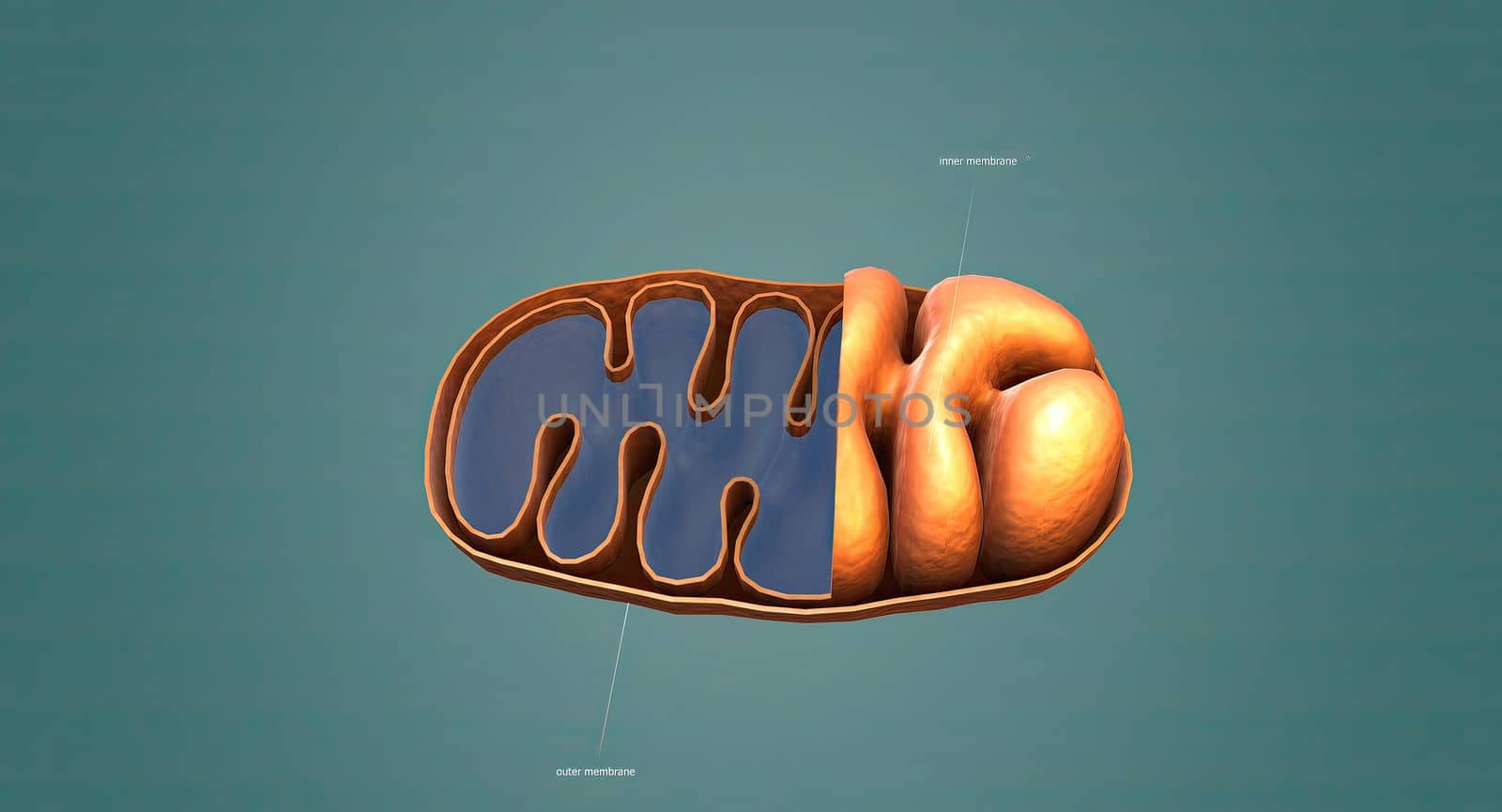
Mitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxMitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.

Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxChromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells

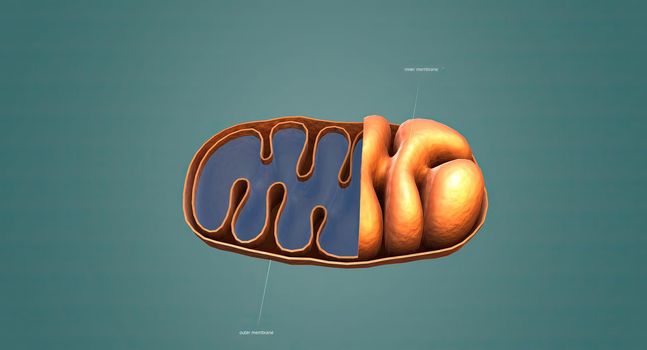
Mitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxMitochondria an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi.
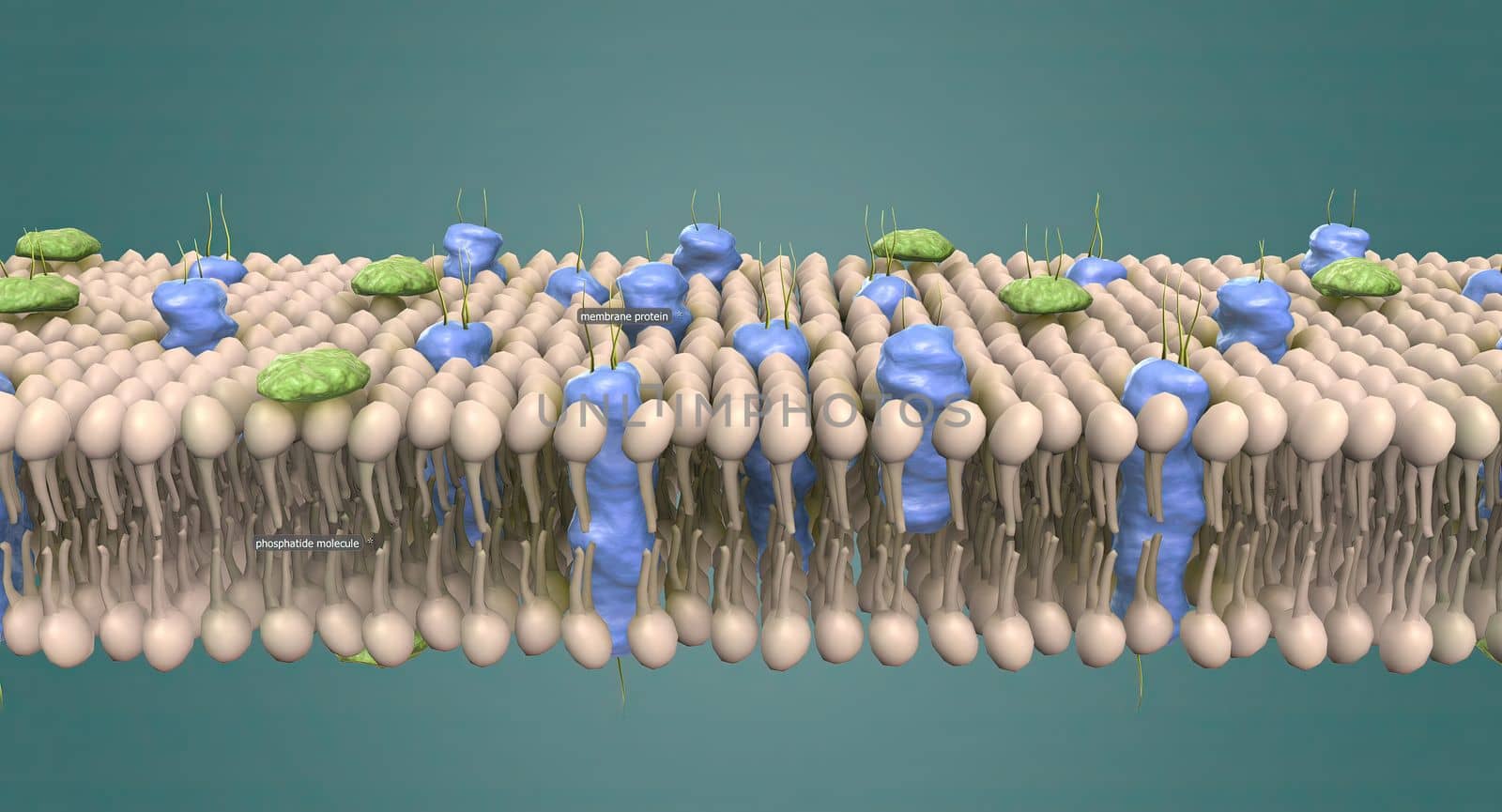
The cell membrane is the thin membrane that surrounds the cell and separates the cell from its surroundings.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxThe cell membrane is the thin membrane that surrounds the cell and separates the cell from its surroundings.
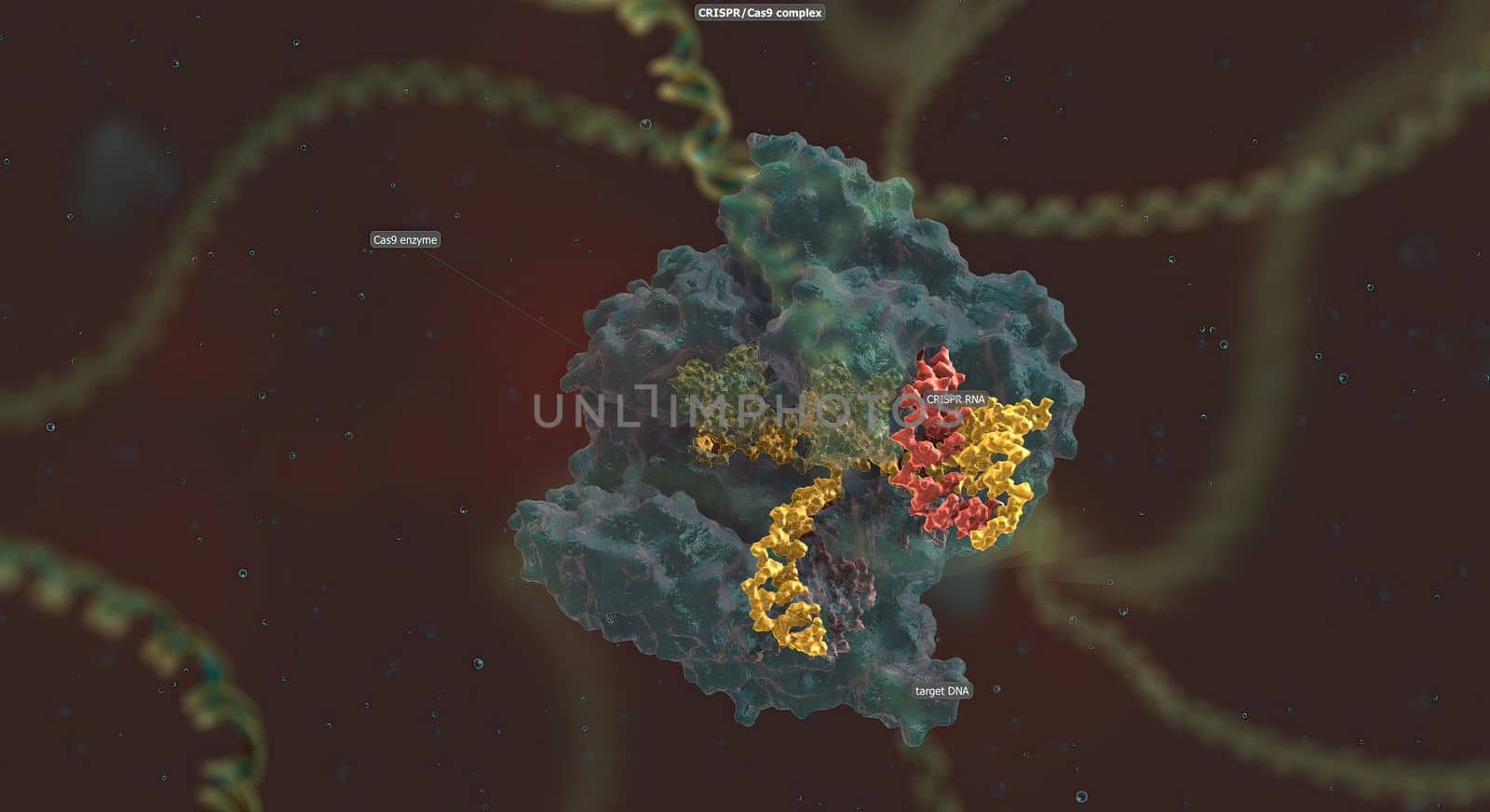
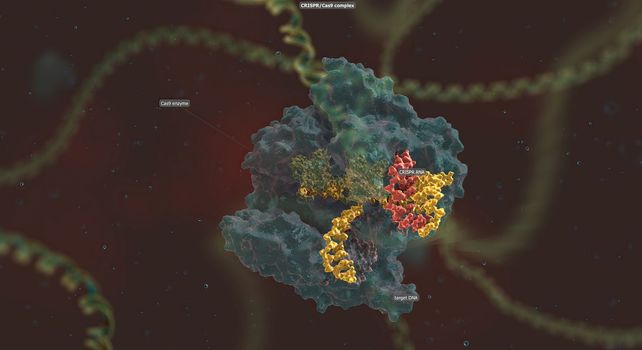
The long RNA backbone binds to the DNA, and the predesigned sequence guides Cas9 to the right spot in the genome.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5562x3030pxThe long RNA backbone binds to the DNA, and the predesigned sequence guides Cas9 to the right spot in the genome.
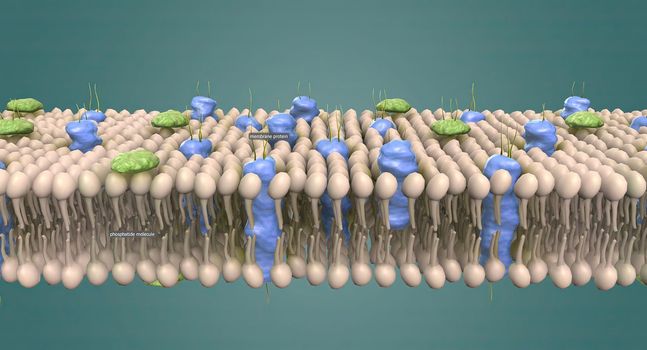
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5426x3068pxA cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
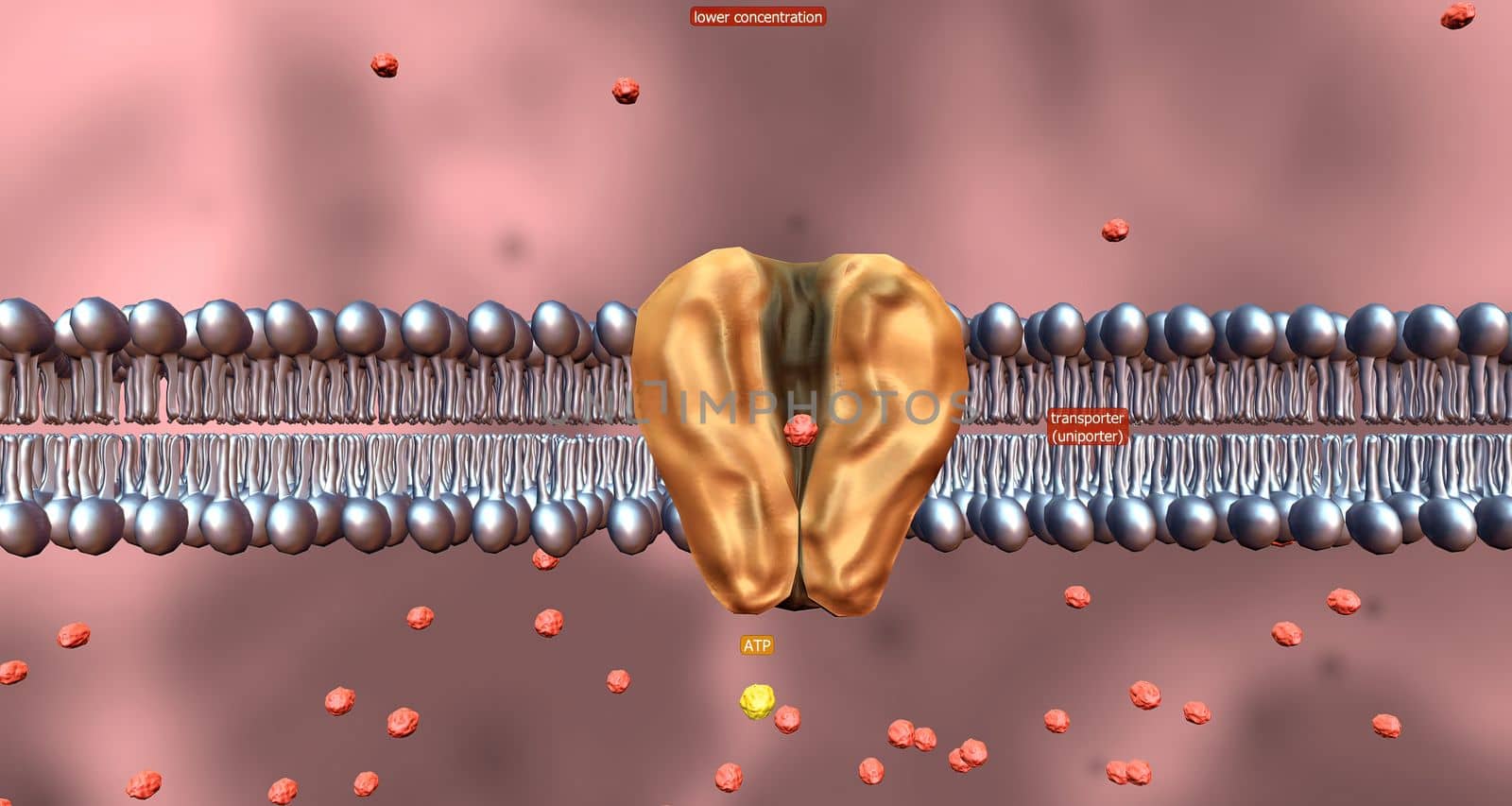
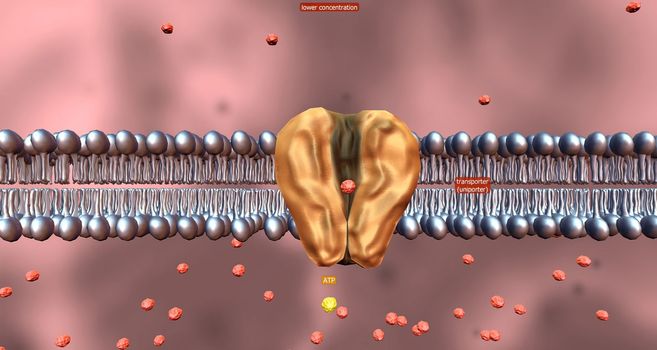
Cell transport refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5506x2936pxCell transport refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane.

A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.

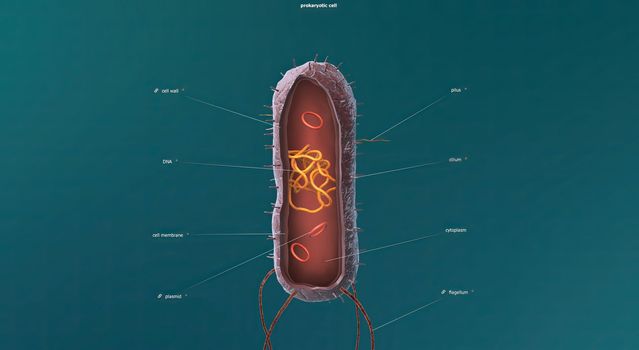
Bacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5426x3068pxBacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
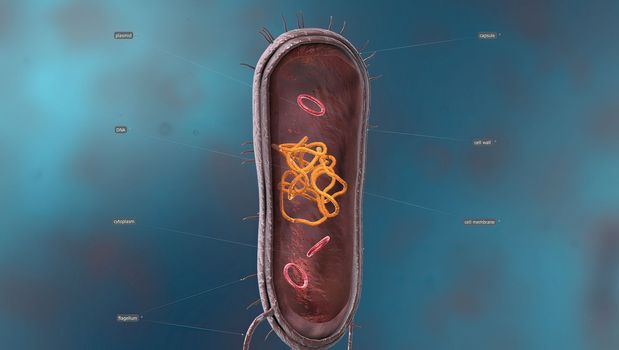

Bacillus is a gram-positive and spore-forming bacterium in the form of rods or rods.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5056x3068pxBacillus is a gram-positive and spore-forming bacterium in the form of rods or rods.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxA virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism

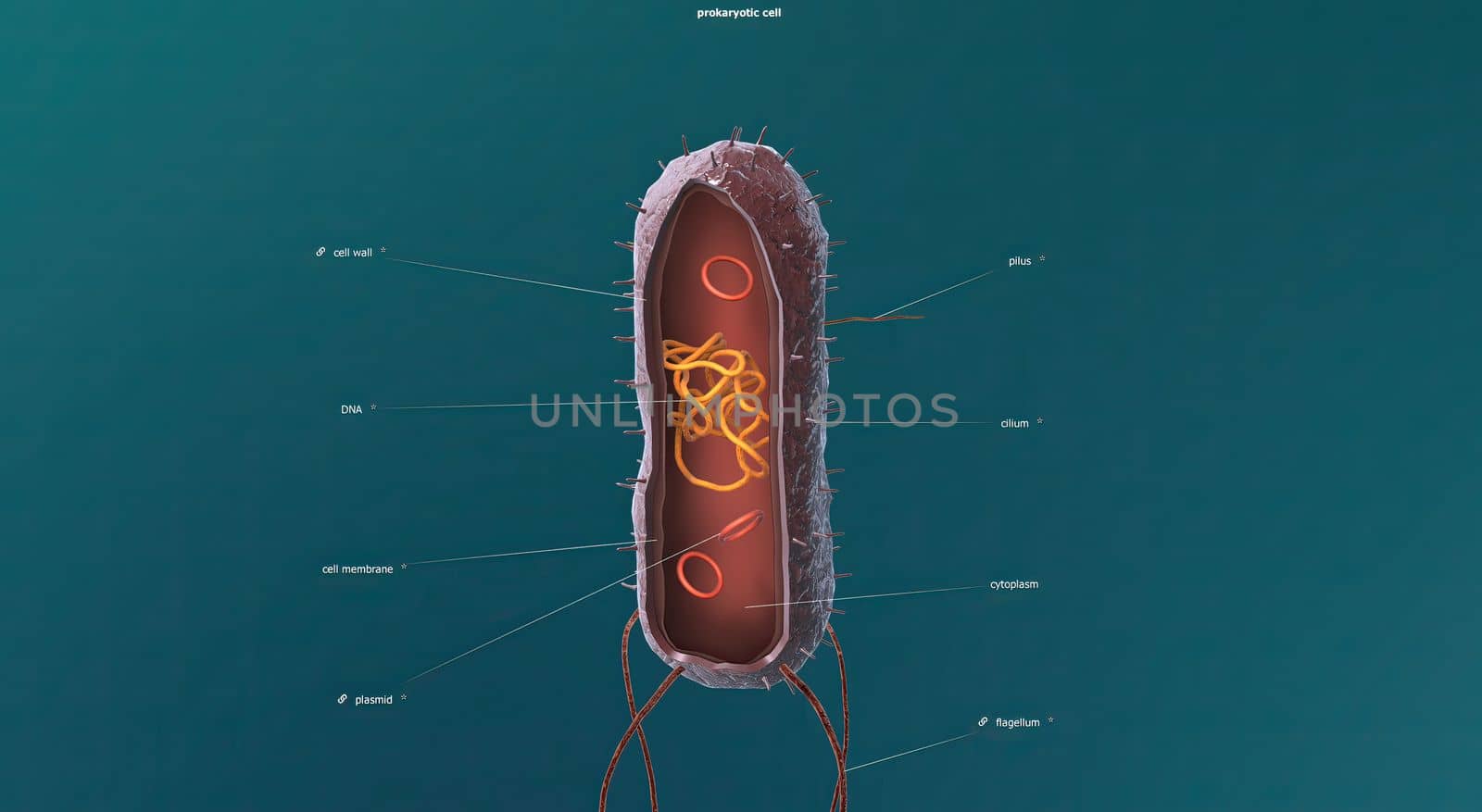
In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxIn cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxIn cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration

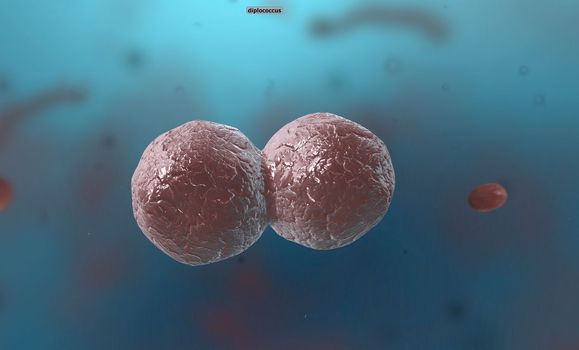
A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
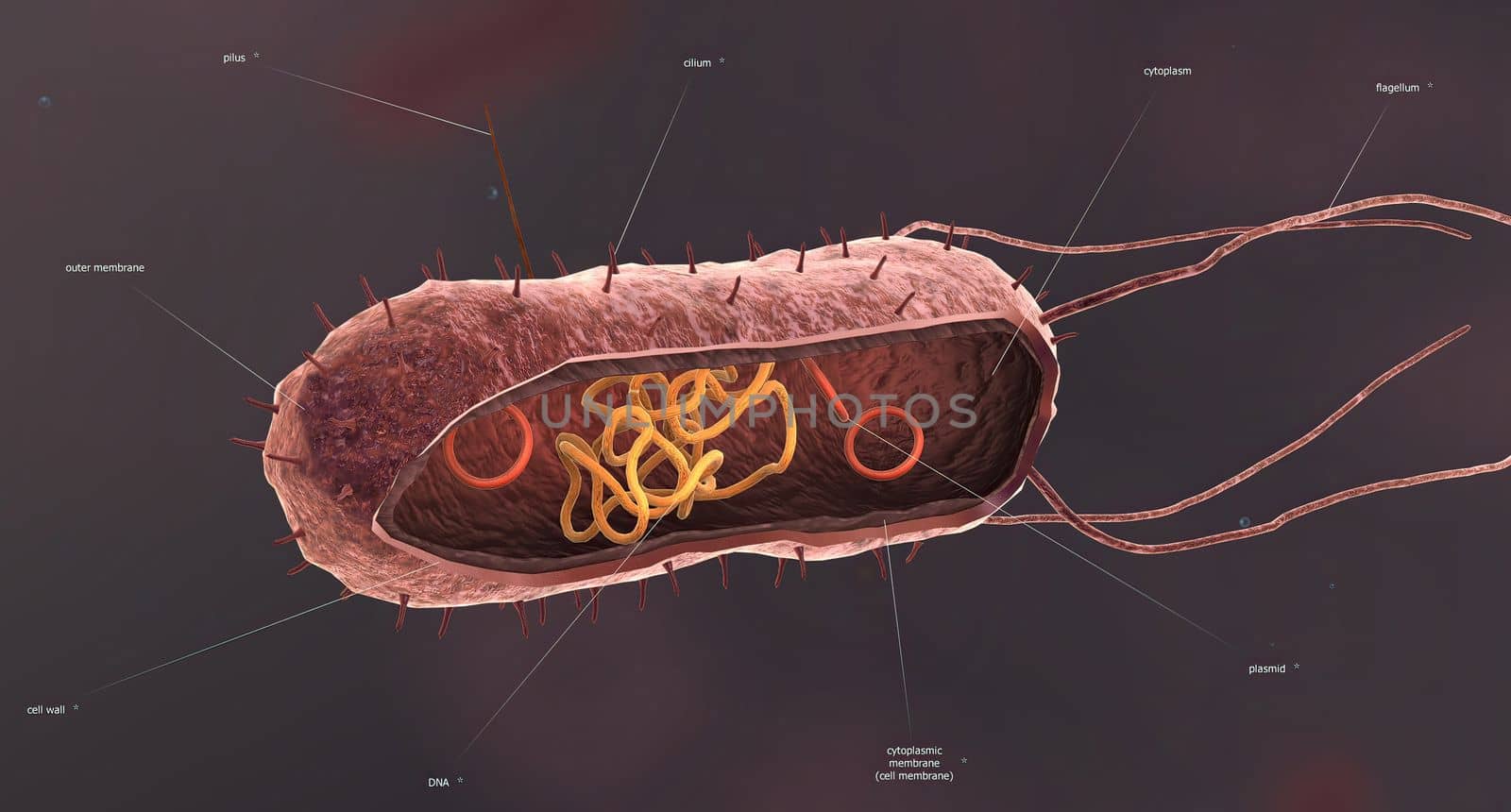
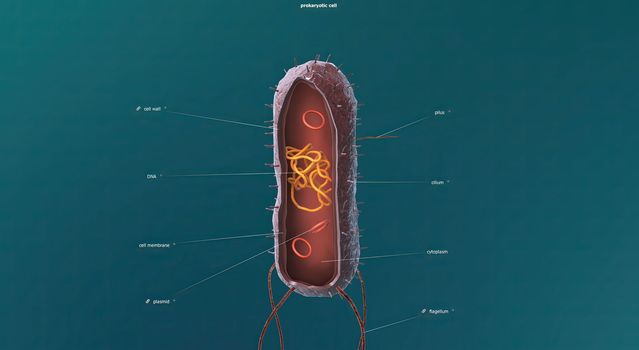
Bacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5726x3076pxBacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
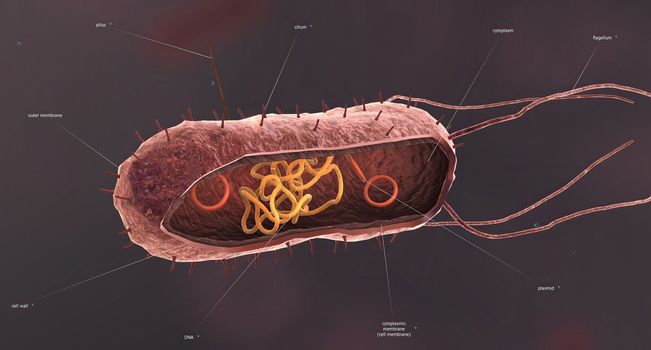

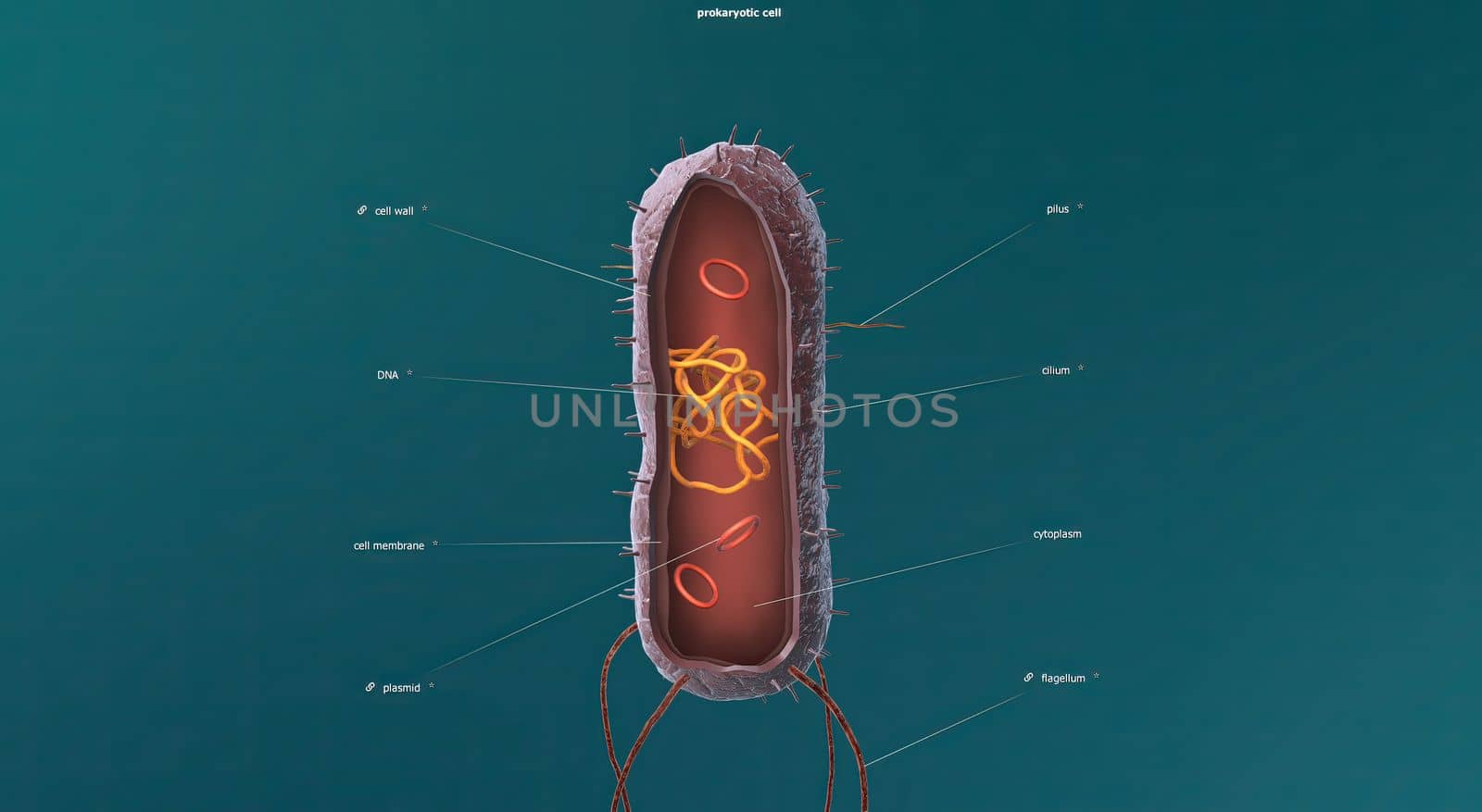
Bacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5426x3068pxBacteria are a simple form of life known as prokaryotes.
In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxIn cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5542x3038pxA virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism

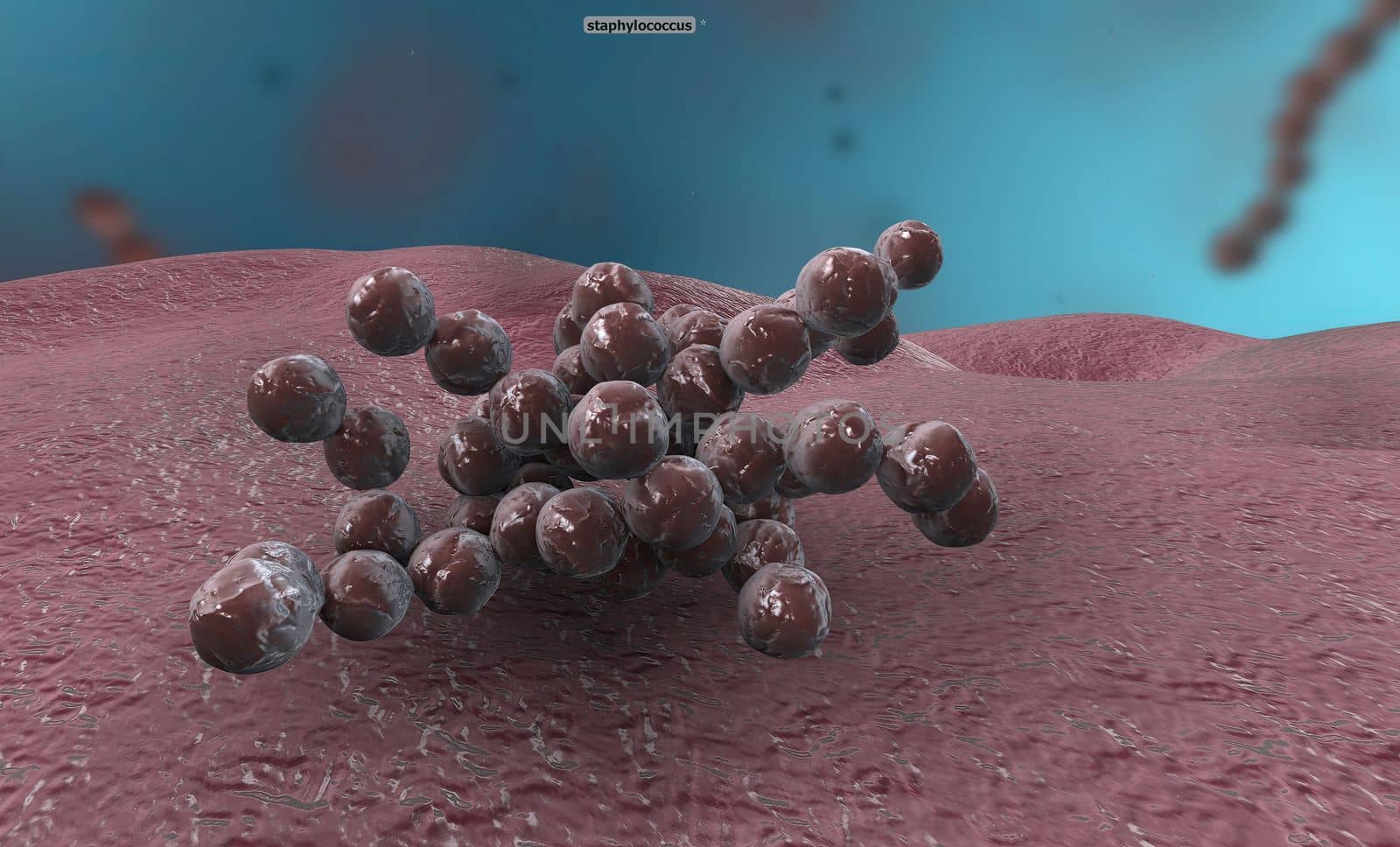
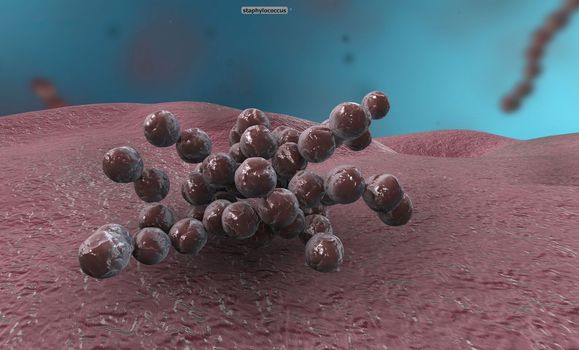
A cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5072x3068pxA cocci are any bacteria or archaeon that have a spherical, oval, or generally round shape.
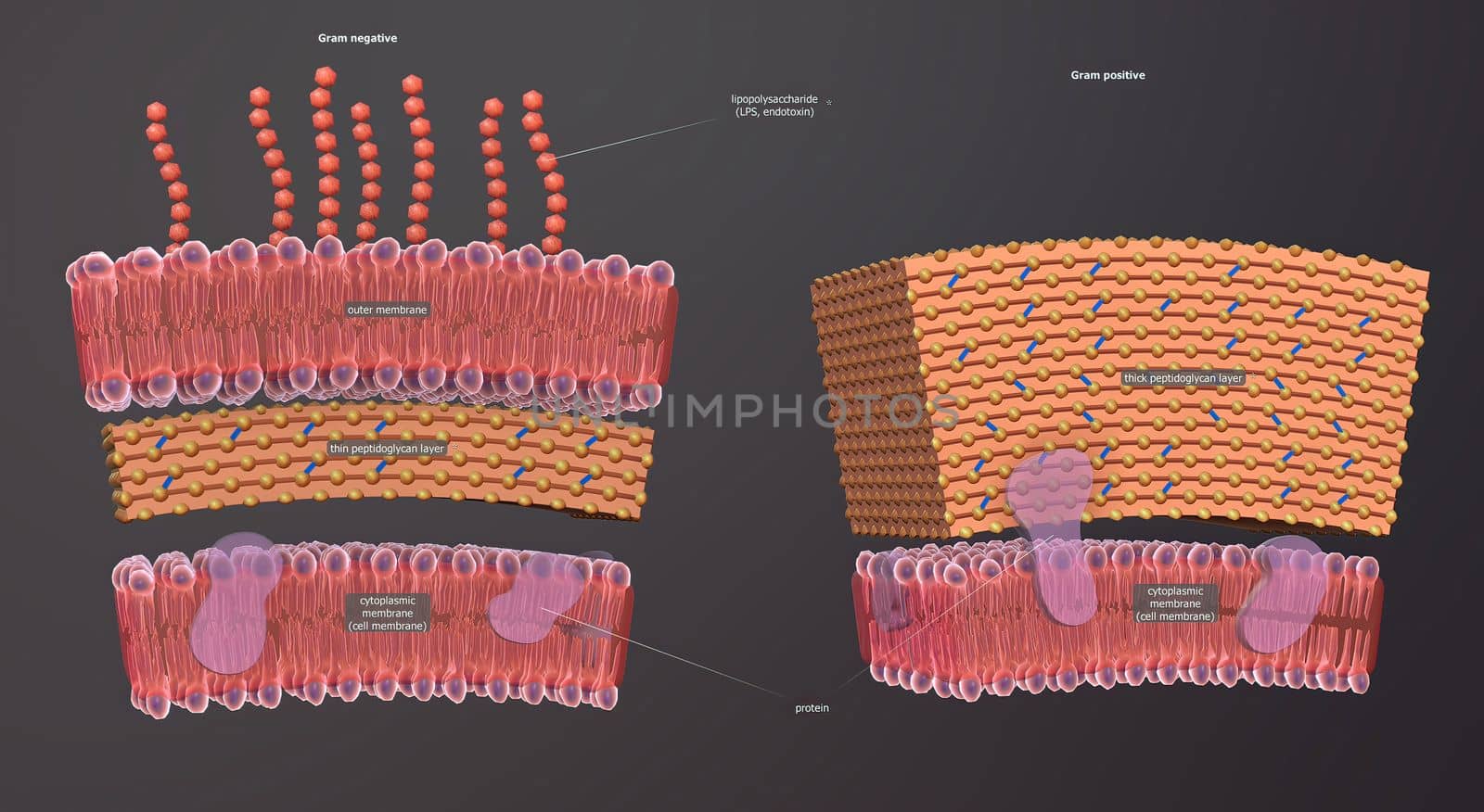
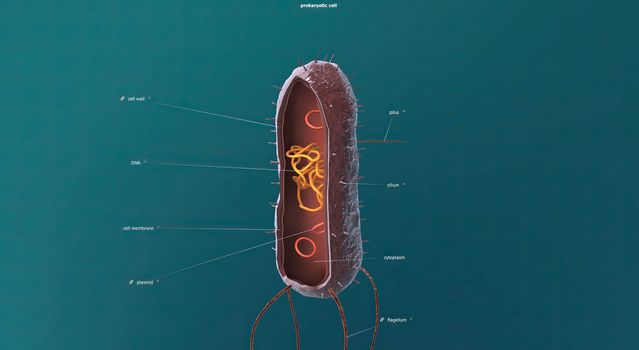
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5602x3066pxA cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.

In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
4678x2894pxIn cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. 3D illustration
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxChromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells
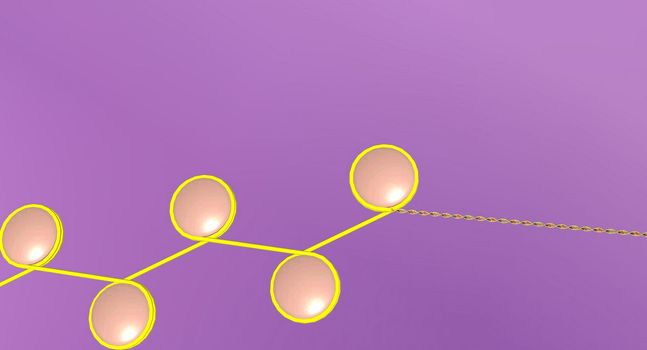

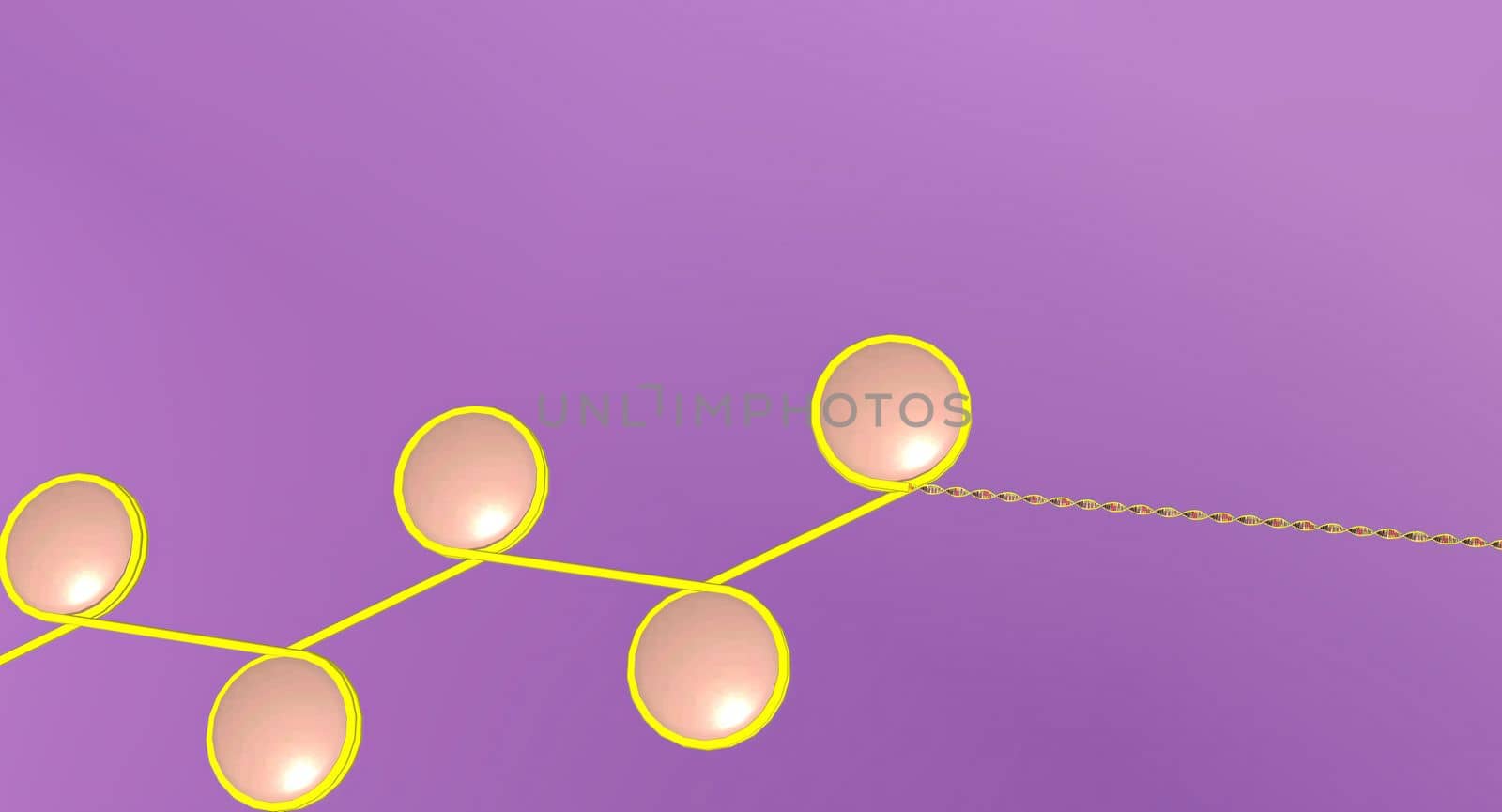
In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
4678x2894pxIn the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes.

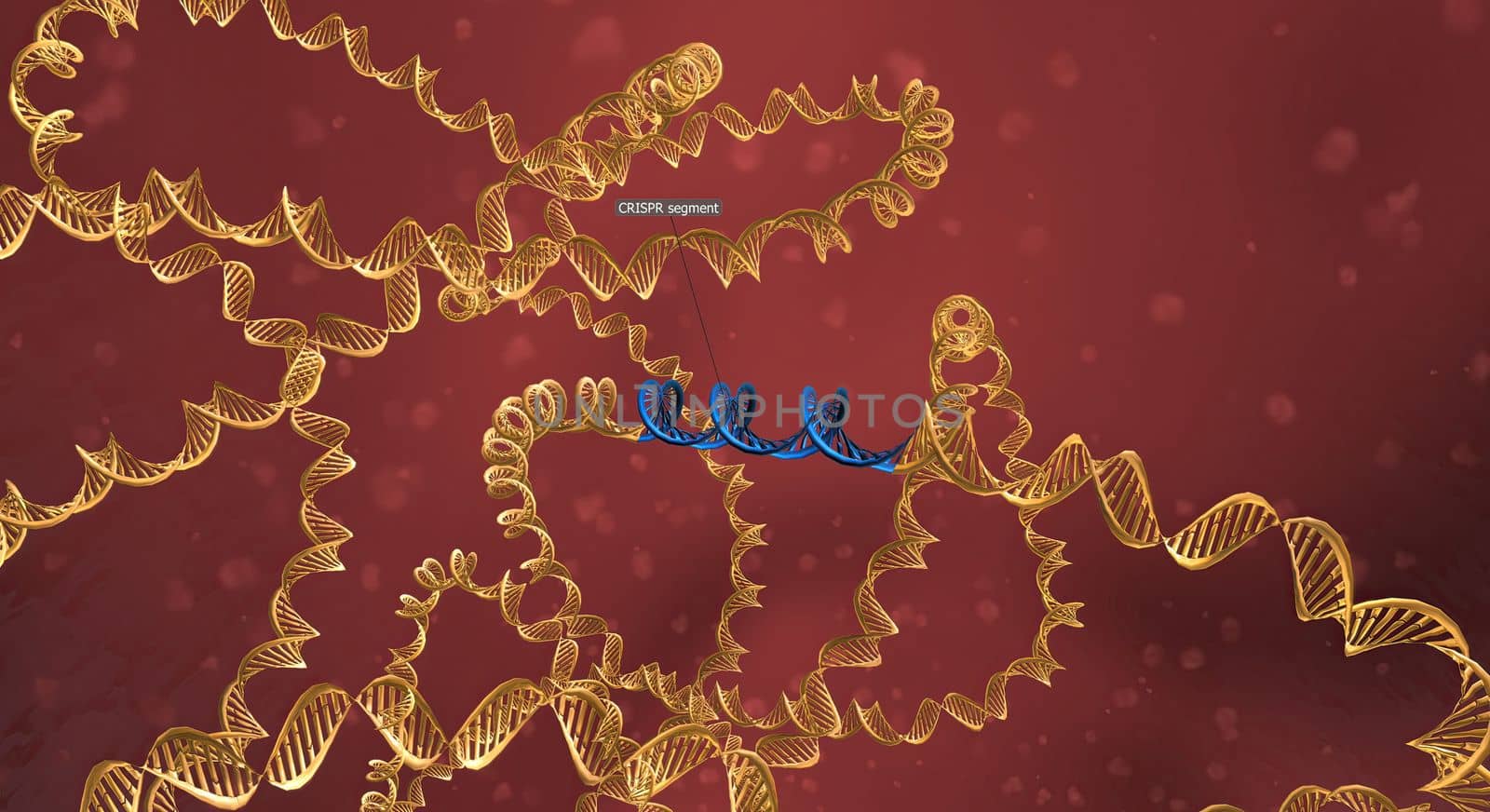
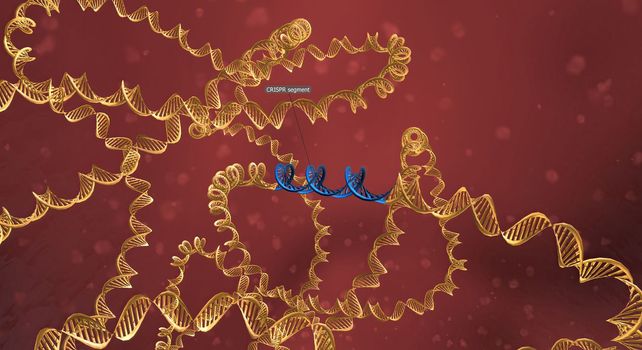
The long RNA backbone binds to the DNA, and the predesigned sequence guides Cas9 to the right spot in the genome. 3D illustration
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5562x3030pxThe long RNA backbone binds to the DNA, and the predesigned sequence guides Cas9 to the right spot in the genome. 3D illustration
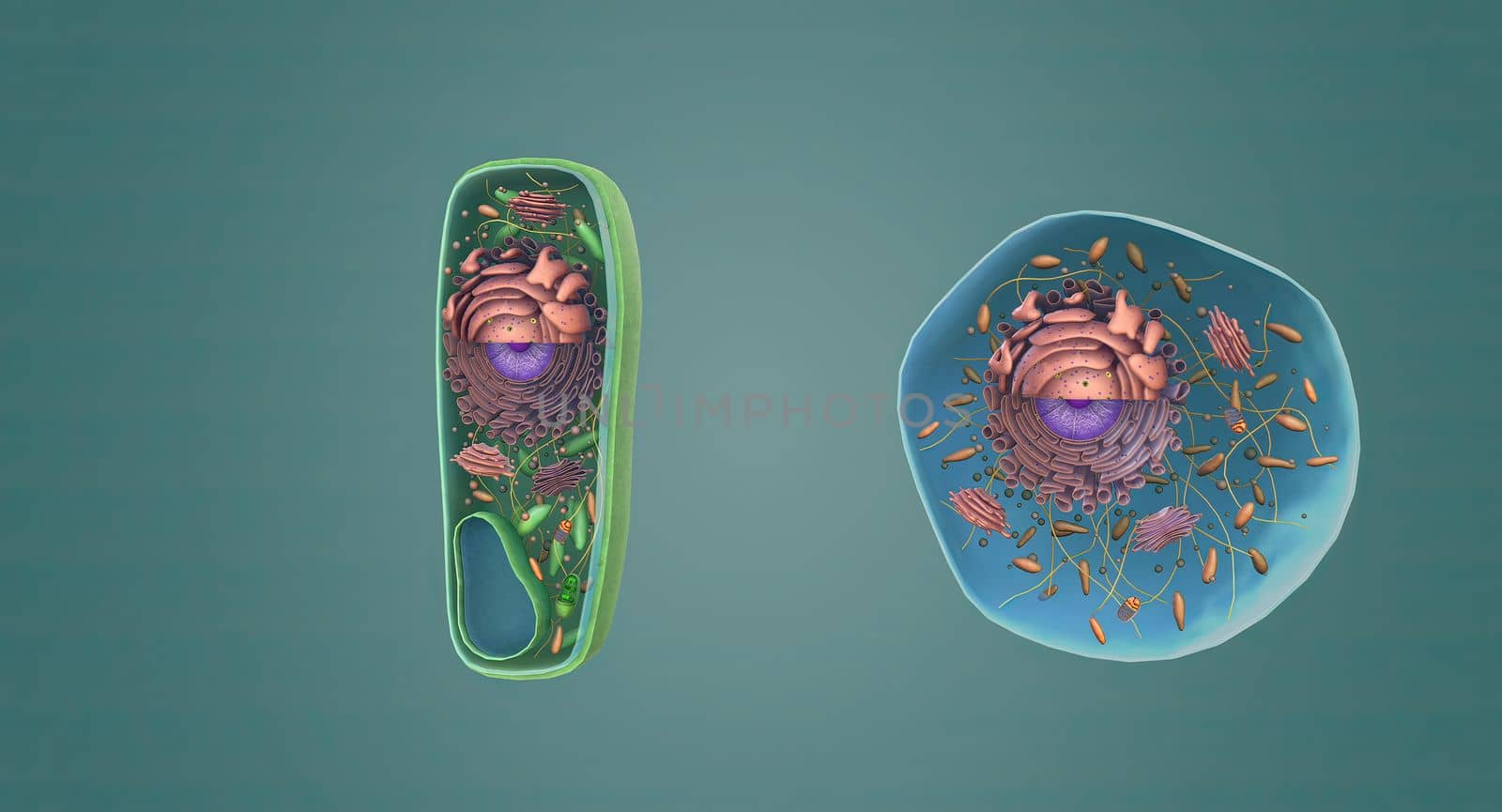
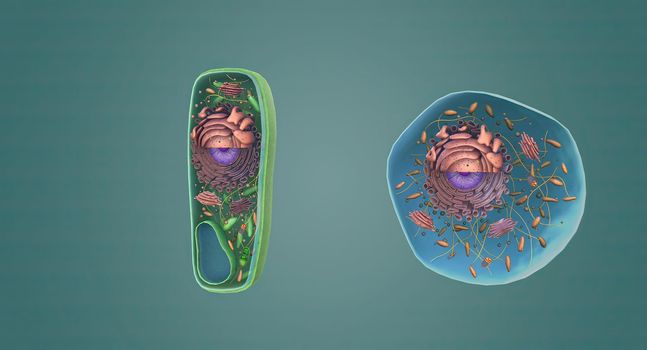
The structure of Plant and Animal Cells
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxThe structure of Plant and Animal Cells
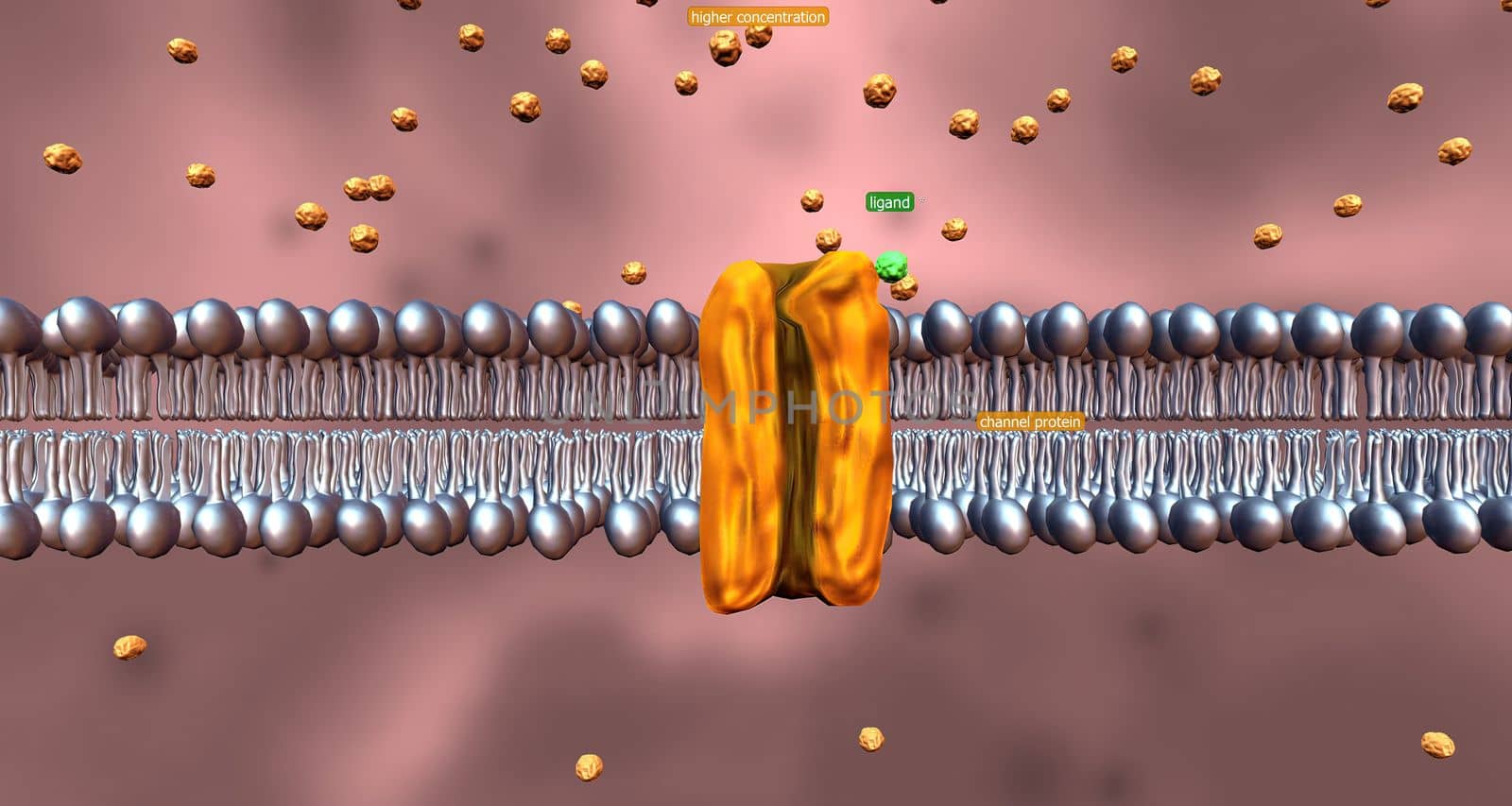
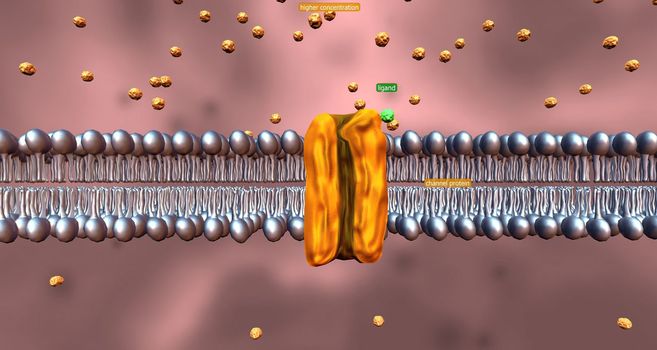
Cell transport refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5506x2936pxCell transport refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
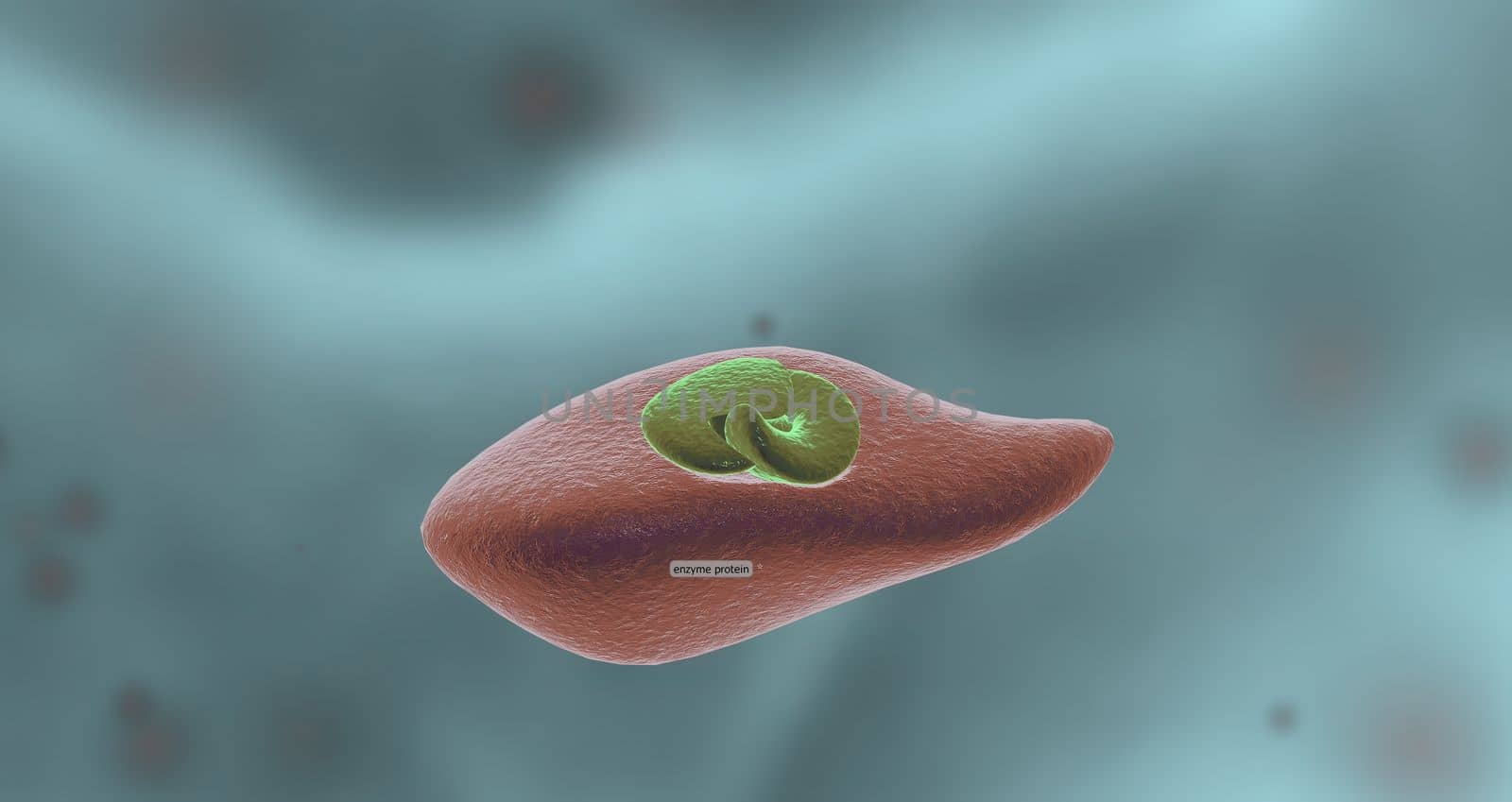
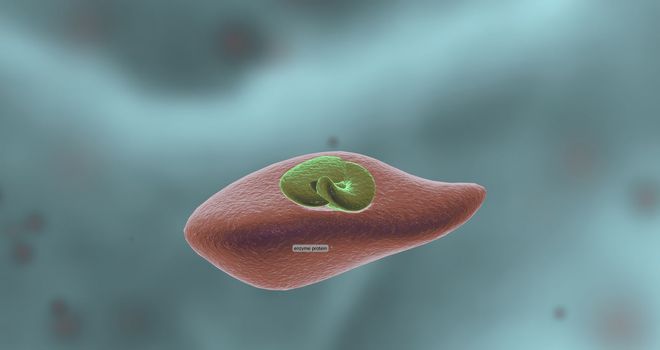
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5530x2936pxEnzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions.
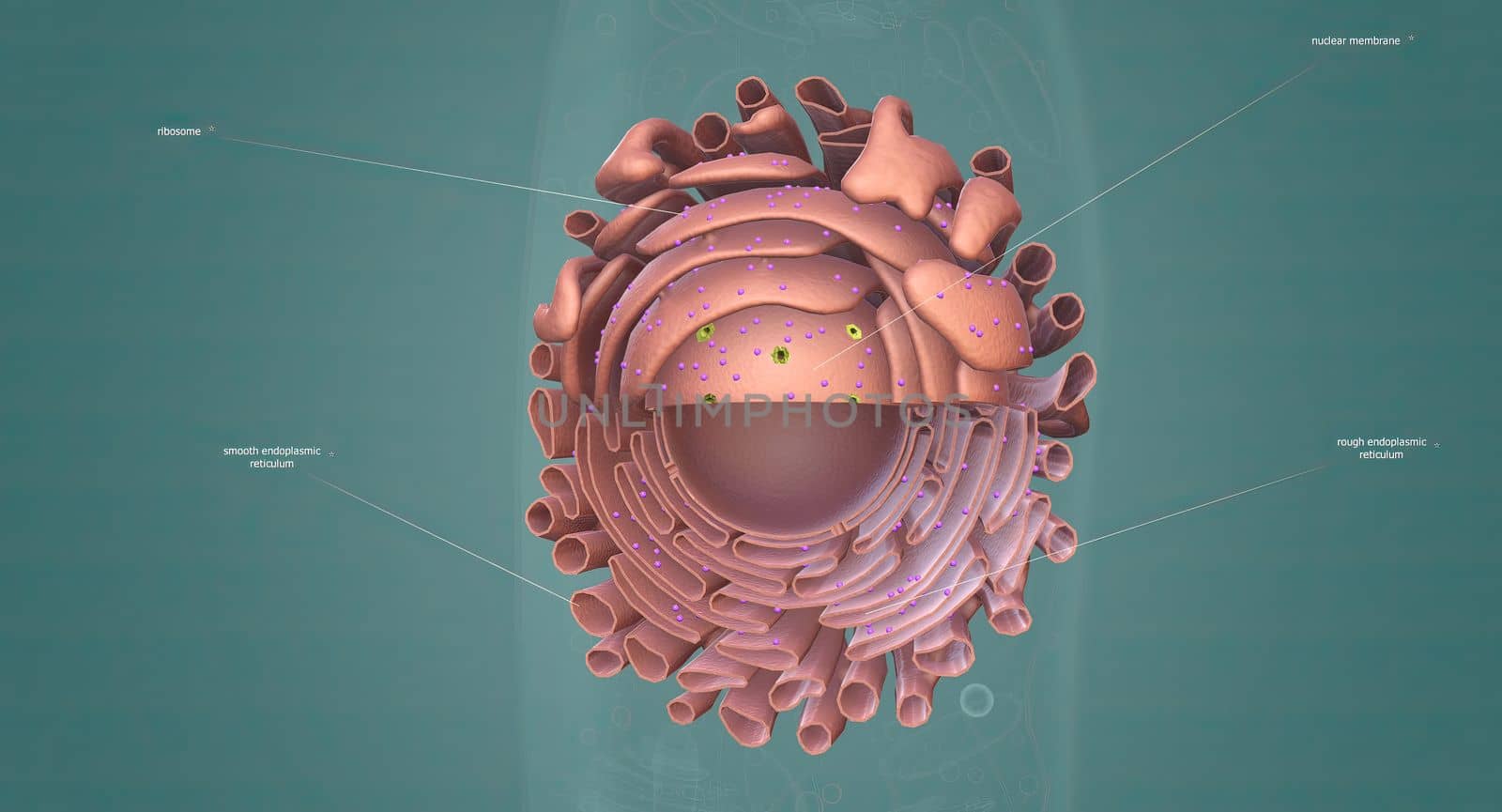
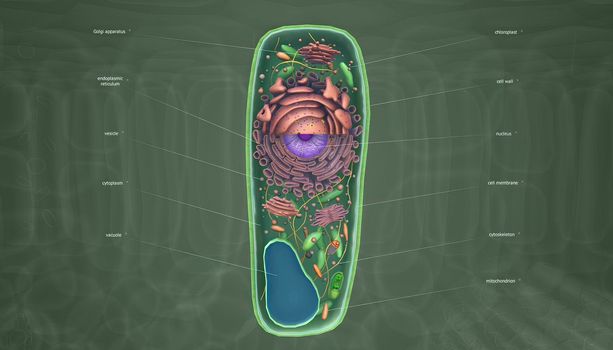
The Golgi complex is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5678x3068pxThe Golgi complex is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells.
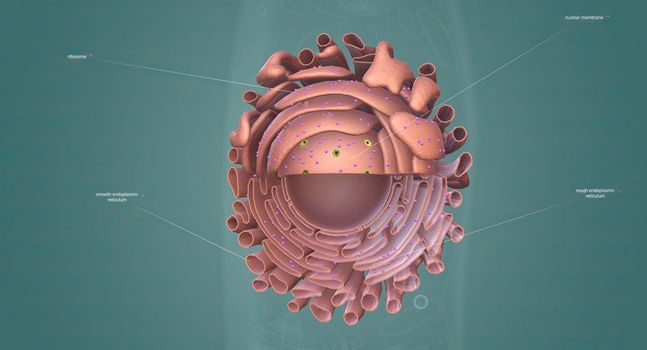

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions.
Stock PhotoUsername
creativepicResolution
5614x2990pxEnzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions.